Phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of inner centromere protein (INCENP) by the Aurora B Kinase stimulates Aurora B kinase activity
- PMID: 12048181
- PMCID: PMC1855214
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C200307200
Phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of inner centromere protein (INCENP) by the Aurora B Kinase stimulates Aurora B kinase activity
Abstract
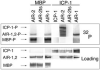
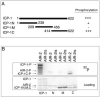
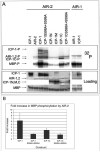
How the events of mitosis are coordinated is not well understood. Intriguing mitotic regulators include the chromosomal passenger proteins. Loss of either of the passengers inner centromere protein (INCENP) or the Aurora B kinase results in chromosome segregation defects and failures in cytokinesis. Furthermore, INCENP and Aurora B have identical localization patterns during mitosis and directly bind each other in vitro. These results led to the hypothesis that INCENP is a direct substrate of Aurora B. Here we show that the Caenorhabditis elegans Aurora B kinase AIR-2 specifically phosphorylated the C. elegans INCENP ICP-1 at two adjacent serines within the carboxyl terminus. Furthermore, the full length and a carboxyl-terminal fragment of ICP-1 stimulated AIR-2 kinase activity. This increase in AIR-2 activity required that AIR-2 phosphorylate ICP-1 because mutation of both serines in the AIR-2 phosphorylation site of ICP-1 abolished the potentiation of AIR-2 kinase activity by ICP-1. Thus, ICP-1 is directly phosphorylated by AIR-2 and functions in a positive feedback loop that regulates AIR-2 kinase activity. Since the Aurora B phosphorylation site within INCENP and the functions of INCENP and Aurora B have been conserved among eukaryotes, the feedback loop we have identified is also likely to be evolutionarily conserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

