Dimethyl sulfoxide blocks herpes simplex virus-1 productive infection in vitro acting at different stages with positive cooperativity. Application of micro-array analysis
- PMID: 12052246
- PMCID: PMC116584
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-2-9
Dimethyl sulfoxide blocks herpes simplex virus-1 productive infection in vitro acting at different stages with positive cooperativity. Application of micro-array analysis
Abstract
Background: Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is frequently used at a concentration of up to 95% in the formulation of antiherpetic agents because of its properties as a skin penetration enhancer. Here, we have analyzed the effect of DMSO on several parameters of Herpes Simplex Virus replication.
Methods: Productive infection levels of HSV-1 were determined by plaque assay or by reporter gene activity, and its DNA replication was estimated by PCR. Transcript levels were evaluated with HSV-specific DNA micro-arrays.
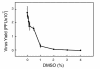
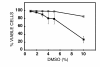
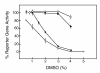
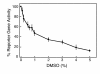
Results: DMSO blocks productive infection in vitro in different cell types with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) from 0.7 to 2% depending upon the multiplicity of infection. The concentration dependence exhibits a Hill coefficient greater than 1, indicating that DMSO blocks productive infection by acting at multiple different points (mechanisms of action) with positive cooperativity. Consistently, we identified at least three distinct temporal target mechanisms for inhibition of virus growth by DMSO. At late stages of infection, DMSO reduces virion infectivity, and markedly inhibits viral DNA replication. A third mode of action was revealed using an oligonucleotide-based DNA microarray system for HSV. These experiments showed that DMSO reduced the transcript levels of many HSV-1 genes; including several genes coding for proteins involved in forming and assembling the virion. Also, DMSO markedly inhibited some but not all early transcripts indicating a previously unknown mode for inhibiting the early phase of HSV transcription-replication cycle.
Conclusion: These observations suggest that DMSO itself may have a role in the anti-herpetic activity of formulations utilizing it as a dispersant.
Figures



References
-
- Whitley RJ, Soong SJ, Dolin R, Galasso GJ, Chien LT, Alford CA. Adenine arabinoside therapy of biopsy-proved herpes simplex encephalitis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antiviral study. N. 1977;297:289–294. - PubMed
-
- Corey L, Spear PG. Infectious with herpes simplex viruses (1). N. 1986;314:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Corey L, Spear PG. Infectious with herpes simplex viruses (2). N. 1986;314:749–757. - PubMed
-
- Nesburn AB. "Report of the Corneal Disease Panel: Vision Research-A National Plan 1983–1987". 1986.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

