Signature tau neuropathology in gray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration
- PMID: 12057909
- PMCID: PMC1850831
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61154-6
Signature tau neuropathology in gray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration
Abstract
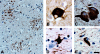
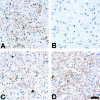
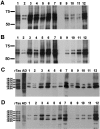
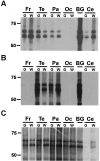
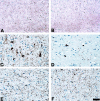
Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) is an adult-onset progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by L-dopa-resistant rigidity, focal cortical deficits, and variable dementia. The neuropathological hallmark of CBD is the deposition of filamentous inclusions in neurons and glia composed of hyperphosphorylated tau with only four microtubule-binding repeats (4R-tau). To characterize the regional burden of tau pathology in CBD, we studied 12 brains with the neuropathological diagnosis of CBD using biochemical and histochemical techniques. Eleven brain regions were evaluated including gray and white matter from frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes and cerebellum as well as basal ganglia. Although the distribution of tau pathology was variable, neuropathological and biochemical data showed a similar burden of tau abnormalities in frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes and basal ganglia of both hemispheres. This included abundant, sarkosyl-insoluble 4R-tau in both gray and white matter of two or more of these cortical regions and basal ganglia, and to a lesser extent, cerebellar white matter. The insoluble tau pathology in gray and white matter showed overlapping but distinct phosphorylated epitopes suggesting cell-type and subcellular localization (ie, cell bodies versus cell processes)-specific differences in tau phosphorylation. In contrast, soluble tau was composed of normal 4R/3R-tau ratios indicating no gross abnormality in tau splicing. Thus, although clinically heterogeneous, CBD is a distinct lobar and basal ganglionic tauopathy with selective aggregation of 4R-tau.
Figures

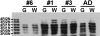
References
-
- Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP, Jr: Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 1968, 18:20-33 - PubMed
-
- Riley DE, Lang AE, Lewis A, Resch L, Ashby P, Hornykiewicz O, Black S: Cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 1990, 40:1203-1212 - PubMed
-
- Gibb WR, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD: Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 1989, 112:1171-1192 - PubMed
-
- Rinne JO, Lee MS, Thompson PD, Marsden CD: Corticobasal degeneration. A clinical study of 36 cases. Brain 1994, 117:1183-1196 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

