Grouping of multiple-lentigines/LEOPARD and Noonan syndromes on the PTPN11 gene
- PMID: 12058348
- PMCID: PMC379170
- DOI: 10.1086/341528
Grouping of multiple-lentigines/LEOPARD and Noonan syndromes on the PTPN11 gene
Abstract
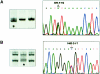
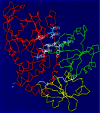
Multiple-lentigines (ML)/LEOPARD (multiple lentigines, electrocardiographic-conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary stenosis, abnormal genitalia, retardation of growth, and sensorineural deafness) syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition--characterized by lentigines and café au lait spots, facial anomalies, cardiac defects--that shares several clinical features with Noonan syndrome (NS). We screened nine patients with ML/LEOPARD syndrome (including a mother-daughter pair) and two children with NS who had multiple café au lait spots, for mutations in the NS gene, PTPN11, and found, in 10 of 11 patients, one of two new missense mutations, in exon 7 or exon 12. Both mutations affect the PTPN11 phosphotyrosine phosphatase domain, which is involved in <30% of the NS PTPN11 mutations. The study demonstrates that ML/LEOPARD syndrome and NS are allelic disorders. The detected mutations suggest that distinct molecular and pathogenetic mechanisms cause the peculiar cutaneous manifestations of the ML/LEOPARD-syndrome subtype of NS.
Figures

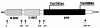
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Deep View Swiss-PdbViewer, http://www.expasy.ch/spdbv/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for ML/LEOPARD syndrome [MIM #151100], NS [MIM #163950], PTPN11 [MIM *176876], CFCS [MIM 115150], NFNS [MIM 601321], Costello syndrome [MIM *218040], Watson syndrome [MIM #193520], and NF1 [MIM *162200])
References
-
- Ahlbom EB, Dahl N, Zetterqvist P, Anneren G (1995) Noonan syndrome with café-au-lait spots and multiple lentigines syndrome are not linked to neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Clin Genet 48:85–89 - PubMed
-
- Blienden LC, Schneeweiss A, Shem-Tov A, Feigel A, Neufeld HN (1983) Unifying link between Noonan’s and Leopard syndromes? Pediatr Cardiol 4:168–169 - PubMed
-
- Carney JA, Headington JT, Su WPD (1986) Cutaneous myxomas: a major component of the complex of myxomas, spotty pigmentation, and endocrine overactivity. Arch Dermatol 122:790–798 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

