Three-dimensional, T1-weighted gradient-echo imaging of the brain with a volumetric interpolated examination
- PMID: 12063232
- PMCID: PMC7976903
Three-dimensional, T1-weighted gradient-echo imaging of the brain with a volumetric interpolated examination
Abstract
Background and purpose: T1-weighted, 3D gradient-echo MR sequences can be optimized for rapid acquisition and improved resolution through asymmetric k-space sampling and interpolation. We compared a volumetric interpolated brain examination (VIBE) sequence with a magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo (MP RAGE) sequence and a 2D T1-weighted spin-echo (SE) sequence.
Methods: Thirty consecutive patients known or suspected to have focal brain lesions underwent postcontrast studies (20 mL of gadopentetate dimeglumine) with VIBE, MP RAGE, and 2D T1-weighted SE imaging. Source and 5-mm VIBE and MP RAGE reformations, and 5-mm T1-weighted SE images were compared qualitatively and by using signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). SNRs in a gadolinium-doped water phantom were also measured for all three sequences.
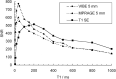
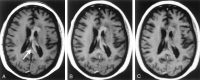
Results: On the source images, SNRs for gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM), and CNRs for WM-to-GM and contrast-enhancing lesion-to-GM were slightly, but significantly higher for the VIBE sequence than for the MP RAGE sequence (P <.05). On 5-mm reformations, WM-to-GM CNR was significantly higher on VIBE and MP RAGE images than on T1-weighted SE images (P <.001), but contrast-enhancing lesion-to-GM CNRs were higher on SE images compared with both gradient-echo sequences (P <.001). Qualitatively, VIBE images showed fewer flow artifacts than did SE and MP RAGE images (P <.05). In the phantom, VIBE SNR was higher than MP RAGE SNR for short T1 relaxation times.
Conclusion: VIBE provides an effective, alternative approach to MP RAGE for fast 3D T1-weighted imaging of the brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of metastatic brain tumor at 3 tesla: utility of T(1)-weighted SPACE compared with 2D spin echo and 3D gradient echo sequence.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2008;7(1):13-21. doi: 10.2463/mrms.7.13. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18460844
-
Three-Dimensional Radial VIBE Sequence for Contrast-Enhanced Brain Imaging: An Alternative for Reducing Motion Artifacts in Restless Children.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018 Apr;210(4):876-882. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18490. Epub 2018 Feb 15. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018. PMID: 29446683
-
MP RAGE: a three-dimensional, T1-weighted, gradient-echo sequence--initial experience in the brain.Radiology. 1992 Mar;182(3):769-75. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.3.1535892. Radiology. 1992. PMID: 1535892
-
Measurement techniques for magnetic resonance imaging of fast relaxing nuclei.MAGMA. 2014 Feb;27(1):5-19. doi: 10.1007/s10334-013-0394-3. Epub 2013 Jul 24. MAGMA. 2014. PMID: 23881004 Review.
-
Pearls and Pitfalls of T1-Weighted Neuroimaging: A Primer for the Clinical Radiologist.Acad Radiol. 2025 May;32(5):2940-2952. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.10.048. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39572296 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the pituitary gland using magnetic resonance imaging: T1-weighted vs. VIBE imaging.Neuroradiol J. 2013 Jun;26(3):297-300. doi: 10.1177/197140091302600307. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Neuroradiol J. 2013. PMID: 23859285 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Utility of 3D Gradient-Echo MR Imaging Sequences through the Filum Compared with Spin-Echo T1 in Children with Concern for Tethered Cord.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023 Mar;44(3):323-327. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7791. Epub 2023 Feb 16. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36797030 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the brain using T1-weighted FLAIR with BLADE compared with a conventional spin-echo sequence.Eur Radiol. 2008 Feb;18(2):337-42. doi: 10.1007/s00330-007-0741-8. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Eur Radiol. 2008. PMID: 17922279 Clinical Trial.
-
State-of-the-art MRI techniques in neuroradiology: principles, pitfalls, and clinical applications.Neuroradiology. 2015 May;57(5):441-67. doi: 10.1007/s00234-015-1500-1. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Neuroradiology. 2015. PMID: 25859832 Review.
-
Flow ghost artifact in slice-encoding direction mimicking vestibular schwannoma in contrast-enhanced 3D spoiled gradient-echo sequence.Eur Radiol. 2004 Mar;14(3):496-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-003-2113-3. Epub 2003 Nov 5. Eur Radiol. 2004. PMID: 14600777
References
-
- Frahm J, Haase A, Matthaei D. Rapid three-dimensional MR imaging using the FLASH technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1986;10:363–368 - PubMed
-
- Runge VM, Wood ML, Kaufman DM, Nelson KL, Traill MR. FLASH: clinical three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. RadioGraphics 1988;8:947–965 - PubMed
-
- Mugler JP 3d, Brookeman JR. Rapid three-dimensional T1-weighted MR imaging with the MP-RAGE sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 1991;1:561–567 - PubMed
-
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Gillan GD, Nitz WR. MP RAGE: a three-dimensional, T1-weighted, gradient-echo sequence—initial experience in the brain. Radiology 1992;182:769–775 - PubMed
-
- Mugler JP 3d, Brookeman JR. Theoretical analysis of gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement in T1-weighted imaging of the brain: comparison of two-dimensional spin-echo and three-dimensional gradient-echo sequences. J Magn Reson Imaging 1993;3:761–769 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
