Fibrinogen binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1: implications for Plasmodium falciparum adhesion
- PMID: 12065544
- PMCID: PMC128049
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3962-3964.2002
Fibrinogen binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1: implications for Plasmodium falciparum adhesion
Abstract
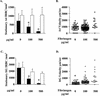
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule implicated in cerebral malaria. We investigated whether fibrinogen affects Plasmodium falciparum binding to ICAM-1, as the ICAM-1 binding sites of P. falciparum and fibrinogen overlap. We show that fibrinogen dramatically reduces P. falciparum adhesion to ICAM-1 under flow conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Baruch, D. I. 1999. Adhesive receptors on malaria-parasitized red cells. Bailliere's Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 12:747-761. - PubMed
-
- Baruch, D. I., J. A. Gormely, C. Ma, R. J. Howard, and B. L. Pasloske. 1996. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 is a parasitized erythrocyte receptor for adherence to CD36, thrombospondin, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:3497-3502. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellamy, R., D. Kwiatkowski, and A. V. Hill. 1998. Absence of an association between intercellular adhesion molecule 1, complement receptor 1 and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms and severe malaria in a West African population. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 92:312-316. - PubMed
-
- Berendt, A. R., D. L. Simmons, J. Tansey, C. I. Newbold, and K. Marsh. 1989. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 341:57-59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

