CpG ODN activates NO and iNOS production in mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7)
- PMID: 12067301
- PMCID: PMC1906257
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01866.x
CpG ODN activates NO and iNOS production in mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7)
Abstract
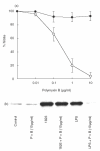
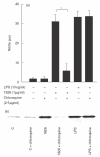
Synthetic CpG containing oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) is recognized for its ability to activate cells to produce several cytokines, such as IL-12 and TNF-alpha. In the present study we have demonstrated that CpG ODN 1826, known for its immunostimulatory activity in the mouse system could, by itself, induce nitric oxide (NO) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) production from mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7). Neutralizing antibody against TNF-alpha was not able to inhibit NO or iNOS production from the CpG ODN 1826-activated macrophages, suggesting that although the TNF-alpha was also produced by CpG ODN-activated macrophages, the production of iNOS was not mediated through TNF-alpha. Although both CpG ODN 1826 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were able to stimulate NO and iNOS production, the exposure time required for maximum production of NO and iNOS for the CpG ODN 1826-activated macrophages was significantly longer than those activated with LPS. These results were due probably to a delay of NF-kappaB translocation, as indicated by the delay of IkappaBalpha degradation. Moreover, the fact that chloroquine abolished NO and iNOS production from the cells treated with CpG ODN 1826 but not from those treated with LPS suggested that the induction of NO and iNOS production from the cells stimulated with CpG ODN (1826) also required endosomal maturation/acidification.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CpG-ODN-induced nitric oxide production is mediated through clathrin-dependent endocytosis, endosomal maturation, and activation of PKC, MEK1/2 and p38 MAPK, and NF-kappaB pathways in avian macrophage cells (HD11).Cell Signal. 2003 Oct;15(10):911-7. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(03)00100-1. Cell Signal. 2003. PMID: 12873704
-
Kinetic studies of the production of nitric oxide (NO) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in macrophages stimulated with Burkholderia pseudomallei endotoxin.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Dec;122(3):324-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01386.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11122236 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of immunostimulatory DNA cures experimental visceral leishmaniasis through nitric oxide up-regulation and T cell activation.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jun;33(6):1508-18. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323671. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12778468
-
Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase activation by immunosuppressive drugs.Curr Drug Metab. 2001 Sep;2(3):315-29. doi: 10.2174/1389200013338405. Curr Drug Metab. 2001. PMID: 11513333 Review.
-
The actions of bacterial DNA on murine macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Oct;66(4):542-8. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.4.542. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10534106 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation-mediated generation and inflammatory potential of human placental cell-free fetal DNA.Placenta. 2020 Apr;93:49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.02.016. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Placenta. 2020. PMID: 32250739 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic application of CpG oligonucleotides augments the early host response and confers protection in acute melioidosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034176. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22448290 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral delivery of brachytherapy and immunotherapy by a thermally triggered polypeptide depot.J Control Release. 2022 Mar;343:267-276. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.01.024. Epub 2022 Jan 22. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35077742 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-based fluorescent probes of NOS2 activity in live brains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 30;117(26):14694-14702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003034117. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32554491 Free PMC article.
-
Dual activation of Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 impairs the efficacy of antitumor vaccines in murine models of metastatic breast cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Sep;143(9):1713-1732. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2421-7. Epub 2017 Apr 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28432455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krieg AM, Yi AK, Schorr J, Davis HL. The role of CpG dinucleotides in DNA vaccine. Trends Microbiol. 1998;6:23–7. - PubMed
-
- Messina JP, Gilkeson GS, Pisetsky DS. Stimulation of in vitro murine lymphocyte proliferation by bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1991;147:1759–64. - PubMed
-
- Sparwasser T, Miethke T, Lipford G, Erdmann A, Hacker H, Heeg K, Wagner H. Macrophages sense pathogens via DNA motive. induction of tumor necrosis factor-α mediated shock. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:1671–9. - PubMed
-
- Sparwasser T, Koch ES, Vabulas RM, et al. Bacterial DNA and immunostimulatory CpG oligonucleotides trigger maturation and activation of murine dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:2045–54. 10.1002/(sici)1521-4141(199806)28:06<2045::aid-immu2045>3.0.co;2-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stacey KJ, Sweet MJ, Hume DA. Macrophages ingest and are activated by bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1996;157:2116–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

