Enhancement of calcium signalling dynamics and stability by delayed modulation of the plasma-membrane calcium-ATPase in human T cells
- PMID: 12068047
- PMCID: PMC2290354
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.016154
Enhancement of calcium signalling dynamics and stability by delayed modulation of the plasma-membrane calcium-ATPase in human T cells
Abstract
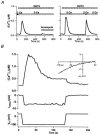
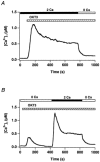
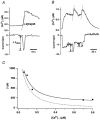
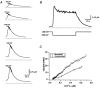
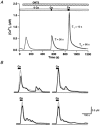
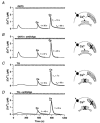
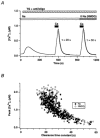
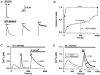
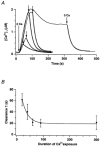
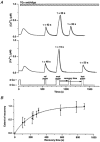
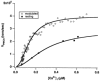
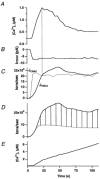
In addition to its homeostatic role of maintaining low resting levels of intracellular calcium ([Ca2+](i)), the plasma-membrane calcium-ATPase (PMCA) may actively contribute to the generation of complex Ca2+ signals. We have investigated the role of the PMCA in shaping Ca2+ signals in Jurkat human leukaemic T cells using single-cell voltage-clamp and calcium-imaging techniques. Crosslinking the T-cell receptor with the monoclonal antibody OKT3 induces a biphasic elevation in [Ca2+](i) consisting of a rapid overshoot to a level > 1 microM, followed by a slow decay to a plateau of approximately 0.5 microM. A similar overshoot was triggered by a constant level of Ca2+ influx through calcium-release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channels in thapsigargin-treated cells, due to a delayed increase in the rate of Ca2+ clearance by the PMCA. Following a rise in [Ca2+](i), PMCA activity increased in two phases: a rapid increase followed by a further calcium-dependent increase of up to approximately fivefold over 10-60 s, termed modulation. After the return of [Ca2+](i) to baseline levels, the PMCA recovered slowly from modulation (tau approximately 4 min), effectively retaining a 'memory' of the previous [Ca2+](i) elevation. Using a Michaelis-Menten model with appropriate corrections for cytoplasmic Ca2+ buffering, we found that modulation extended the dynamic range of PMCA activity by increasing both the maximal pump rate and Ca2+ sensitivity (reduction of K(M)). A simple flux model shows how pump modulation and its reversal produce the initial overshoot of the biphasic [Ca2+](i) response. The modulation of PMCA activity enhanced the stability of Ca2+ signalling by adjusting the efflux rate to match influx through CRAC channels, even at high [Ca2+](i) levels that saturate the transport sites and would otherwise render the cell defenceless against additional Ca2+ influx. At the same time, the delay in modulation enables small Ca2+ fluxes to transiently elevate [Ca2+](i), thus enhancing Ca2+ signalling dynamics.
Figures
References
-
- Almers W, Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Letters. 1985;192:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Arnaudeau S, Kelley WL, Walsh JV, Jr, Demaurex N. Mitochondria recycle Ca2+ to the endoplasmic reticulum and prevent the depletion of neighboring endoplasmic reticulum regions. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276:29430–29439. - PubMed
-
- Babcock DF, Hille B. Mitochondrial oversight of cellular Ca2+ signaling. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 1998;8:398–404. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanyam M, Gardner JP. Protein kinase C modulates cytosolic free calcium by stimulating calcium pump activity in Jurkat T cells. Cell Calcium. 1995;18:526–541. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanyam M, Kimura M, Aviv A, Gardner JP. Kinetics of calcium transport across the lymphocyte plasma membrane. American Journal of Physiology. 1993;265:C321–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

