Enzymes associated with reductive activation and action of nitazoxanide, nitrofurans, and metronidazole in Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 12069963
- PMCID: PMC127316
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2116-2123.2002
Enzymes associated with reductive activation and action of nitazoxanide, nitrofurans, and metronidazole in Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
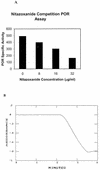
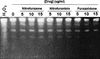
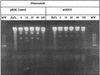
Nitazoxanide (NTZ) is a redox-active nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide prodrug that kills Helicobacter pylori and also many anaerobic bacterial, protozoan, and helminthic species. Here we describe development and use of a spectrophotometric assay, based on nitroreduction of NTZ at 412 nm, to identify H. pylori enzymes responsible for its activation and mode of action. Three enzymes that reduce NTZ were identified: two related NADPH nitroreductases, which also mediate susceptibility to metronidazole (MTZ) (RdxA and FrxA), and pyruvate oxidoreductase (POR). Recombinant His-tagged RdxA, FrxA, and POR, overexpressed in nitroreductase-deficient Escherichia coli, each rapidly reduced NTZ, whereas only FrxA and to a lesser extent POR reduced nitrofuran substrates (furazolidone, nitrofurantoin, and nitrofurazone). POR exhibited no MTZ reductase activity either in extracts of H. pylori or following overexpression in E. coli; RdxA exhibited no nitrofuran reductase activity, and FrxA exhibited no MTZ reductase activity. Analysis of mutation to rifampin resistance (Rif(r)) indicated that NTZ was not mutagenic and that nitrofurans were only weakly mutagenic. Alkaline gel DNA electrophoresis indicated that none of these prodrugs caused DNA breakage. In contrast, MTZ caused DNA damage and was strongly mutagenic. We conclude that POR, an essential enzyme, is responsible for most or all of the bactericidal effects of NTZ against H. pylori. While loss-of-function mutations in rdxA and frxA produce a Mtz(r) phenotype, they do not contribute much to the innate susceptibility of H. pylori to NTZ or nitrofurans.
Figures

References
-
- Broekhuysen, J., A. Stockis, R. L. Lins, J. De Graeve, and J. F. Rossignol. 2000. Nitazoxanide: pharmacokinetics and metabolism in man. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:387-394. - PubMed
-
- Bryant, C., and M. DeLuca. 1991. Purification and characterization of an oxygen-insensitive NAD(P)H nitroreductase from Enterobacter cloacae. J. Biol. Chem. 266:4119-4125. - PubMed
-
- Chalker, A. F., H. W. Minehart, N. J. Hughes, K. K. Koretke, M. A. Lonetto, K. K. Brinkman, P. V. Warren, A. Lupas, M. J. Stanhope, J. R. Brown, and P. S. Hoffman. 2001. Systematic identification of selective essential genes in Helicobacter pylori by genome prioritization and allelic replacement mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 183:1259-1268. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doumbo, O., J. F. Rossignol, E. Pichard, H. A. Traore, T. M. Dembele, M. Diakite, F. Traore, and D. A. Diallo. 1997. Nitazoxanide in the treatment of cryptosporidial diarrhea and other intestinal parasitic infections associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in tropical Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 56:637-639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

