Antiretrovirus activity of a novel class of acyclic pyrimidine nucleoside phosphonates
- PMID: 12069973
- PMCID: PMC127315
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2185-2193.2002
Antiretrovirus activity of a novel class of acyclic pyrimidine nucleoside phosphonates
Abstract
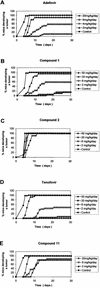
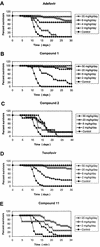
A novel class of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates has been discovered in which the base consists of a pyrimidine preferably containing an amino group at C-2 and C-4 and a 2-(phosphonomethoxy)ethoxy (PMEO) or a 2-(phosphonomethoxy)propoxy (PMPO) group at C-6. The 6-PMEO 2,4-diaminopyrimidine (compound 1) and 6-PMPO 2,4-diaminopyrimidine (compound 11) derivatives showed potent activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in the laboratory (i.e., CEM and MT-4 cells) and in primary (i.e., peripheral blood lymphocyte and monocyte/macrophage) cell cultures and pronounced activity against Moloney murine sarcoma virus in newborn NMRI mice. Their in vitro and in vivo antiretroviral activity was comparable to that of reference compounds 9-[(2-phosphonomethoxy)ethyl]adenine (adefovir) and (R)-9-[(2-phosphonomethoxy)-propyl]adenine (tenofovir), and the enantiospecificity of (R)- and (S)-PMPO pyrimidine derivatives as regards their antiretroviral activity was identical to that of the classical (R)- and (S)-9-(2-phosphonomethoxy)propyl purine derivatives. The prototype PMEO and PMPO pyrimidine analogues were relatively nontoxic in cell culture and did not markedly interfere with host cell macromolecular (i.e., DNA, RNA, or protein) synthesis. Compounds 1 and 11 should be considered attractive novel pyrimidine nucleotide phosphonate analogues to be further pursued for their potential as antiretroviral agents in the clinical setting.
Figures
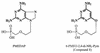
Similar articles
-
Pronounced in vitro and in vivo antiretroviral activity of 5-substituted 2,4-diamino-6-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)ethoxy] pyrimidines.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Jan;59(1):80-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl454. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17124193
-
6-[2-phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidines: a new class of acyclic pyrimidine nucleoside phosphonates with antiviral activity.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004 Oct;23(8-9):1321-7. doi: 10.1081/NCN-200027573. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004. PMID: 15571252
-
Antiviral potential of a new generation of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates, the 6-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidines.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005;24(5-7):331-41. doi: 10.1081/ncn-200059772. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005. PMID: 16247948
-
Amino Acid Ester Prodrugs of Nucleoside and Nucleotide Antivirals.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(10):818-833. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170216151601. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28215138 Review.
-
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV infection.Clin Ther. 2002 Oct;24(10):1515-48. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(02)80058-3. Clin Ther. 2002. PMID: 12462284 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential of the South African plant Tulbaghia Violacea Harv for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88417-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962120 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient microwave-assisted synthesis and biological properties of polysubstituted pyrimidinyl- and 1,3,5-triazinylphosphonic acids.Tetrahedron. 2012 Jan 21;68(3):865-871. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2011.11.040. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Tetrahedron. 2012. PMID: 32287424 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of 5-iodopyrimidine analogs.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009 Nov;71(6):672-7. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.59551. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009. PMID: 20376222 Free PMC article.
-
Acyclic nucleoside bisphosphonates: synthesis and properties of chiral 2-amino-4,6-bis[(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]pyrimidines.Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jun;44(6):2408-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.09.031. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 18992968 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Synthesis of Nucleoside Phosphonate Analogs Using Olefin Cross-metathesis.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(16):3193-3242. doi: 10.2174/0109298673280546240106123000. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38693731 Review.
References
-
- Aduma, P. P., M. C. Connelly, R. V. Srinivas, and A. Fridland. 1995. Metabolic diversity and antiviral activities of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates. Mol. Pharmacol. 47:816-822. - PubMed
-
- Andrei, G., R. Snoeck, D. Schols, P. Goubau, J. Desmyter, and E. De Clercq. 1991. Comparative activity of selected antiviral compounds against clinical isolates of human cytomegalovirus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 10:1026-1033. - PubMed
-
- Andrei, G., R. Snoeck, P. Goubau, J. Desmyter, and E. De Clercq. 1992. Comparative activity of various compounds against clinical strains of herpes simplex virus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 11:143-151. - PubMed
-
- Balzarini, J., and E. De Clercq. 1994. Biochemical pharmacology of nucleoside analogs active against HIV, p. 751-772. In S. Broder, T. C. Merigan, and D. Bolognesi (ed.), Textbook of AIDS medicine. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
-
- Balzarini, J., L. Naesens, P. Herdewijn, I. Rosenberg, A. Holý, R. Pauwels, M. Baba, D. G. Johns, and E. De Clercq. 1989. Marked in vivo antiretrovirus activity of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine, a selective anti-human immunodeficiency virus agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:332-336. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

