Novel class 1 integron (InS21) carrying blaCTX-M-2 in Salmonella enterica serovar infantis
- PMID: 12069984
- PMCID: PMC127285
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2257-2261.2002
Novel class 1 integron (InS21) carrying blaCTX-M-2 in Salmonella enterica serovar infantis
Abstract
The genetic organization of the region coding for CTX-M-2 in Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis was determined by PCR mapping. This gene seems to have been mobilized from the Kluyvera ascorbata chromosome to a complex sulI-type integron, similar to In6 and In7.
Figures

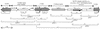

References
-
- Arlet, G., G. Brami, D. Décrè, A. Flippo, O. Gaillot, P. H. Lagrange, and A. Philippon. 1995. Molecular chracterisation by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism of TEM β-lactamases. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 134:203-208. - PubMed
-
- Bantar, C., A. Famiglietti, M. Goldberg, Antimicrobial Committee, et al. 2000. Three-year surveillance study of nosocomial bacterial resistance in Argentina. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 4:85-90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

