Inhibition of penicillinase by epigallocatechin gallate resulting in restoration of antibacterial activity of penicillin against penicillinase-producing Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 12069986
- PMCID: PMC127279
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2266-2268.2002
Inhibition of penicillinase by epigallocatechin gallate resulting in restoration of antibacterial activity of penicillin against penicillinase-producing Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
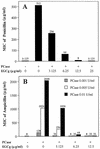
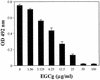
The combination of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg, a main constituent of tea catechins) with penicillin showed synergism against 21 clinical isolates of penicillinase-producing Staphylococcus aureus. Besides binding directly to peptidoglycan, the inhibition of penicillinase activity by EGCg is responsible for the synergism. EGCg inhibited the penicillinase activity in a dose-dependent fashion, with a 50% inhibitory concentration of 10 microg/ml.
Figures
References
-
- Chaibi, E. B., D. Sirot, G. Paul, and R. Labia. 1999. Inhibitor-resistant TEM β-lactamase: phenotypic, genetic and biochemical characteristics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 43:447-458. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L., M. J. Lee, H. Li, and C. S. Yang. 1997. Absorption, distribution, elimination of tea polyphenols in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 25:1045-1050. - PubMed
-
- Heritage, J., F. H. M'Zali, D. Gascoyne-Binzi, and P. M. Hawkey. 1999. Evolution and spread of SHV extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Gram-negative bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 44:309-318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

