GF120918, a P-glycoprotein modulator, increases the concentration of unbound amprenavir in the central nervous system in rats
- PMID: 12069991
- PMCID: PMC127290
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2284-2286.2002
GF120918, a P-glycoprotein modulator, increases the concentration of unbound amprenavir in the central nervous system in rats
Abstract
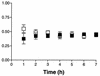
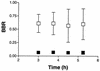
The goal of this study was to determine the distribution of unbound amprenavir in the central nervous system (CNS) of rats. The concentration of unbound amprenavir in the extracellular fluid of the brain and the blood was examined in the presence and absence of the MDR modulator GF120918 by microdialysis. The brain-to-blood ratio of amprenavir in the absence and presence of GF120918 was found to be significantly different (P < 0.003; 0.076 and 0.617, respectively). The use of the MDR modulator GF120918 could potentially increase the penetration of human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors into the CNS.
Figures
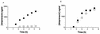
References
-
- Allen, D. D., P. A. Crooks, and R. A. Yokel. 1992. 4-Trimethylammonium antipyrine: a quaternary ammonium nonradionuclide marker for blood-brain barrier integrity during in vivo microdialysis. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 28:129-135. - PubMed
-
- Bellamy, W. T. 1996. P-glycoproteins and multidrug resistance. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36:161-183. - PubMed
-
- Bouw, M. R., and M. Hammarlund-Udenaes. 1998. Methodological aspects of the use of a calibrator in in vivo microdialysis—further development of the retrodialysis method. Pharm. Res. 15:1673-1679. - PubMed
-
- Burgio, D. E., M. P. Gosland, and P. J. McNamara. 1996. Modulation effects of cyclosporine on etoposide pharmacokinetics and CNS distribution in the rat utilizing microdialysis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 51:987-992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

