Neuroprotection and reduced proliferation of microglia in ribavirin-treated bornavirus-infected rats
- PMID: 12069992
- PMCID: PMC127284
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2287-2291.2002
Neuroprotection and reduced proliferation of microglia in ribavirin-treated bornavirus-infected rats
Abstract
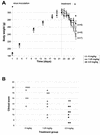
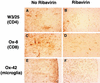
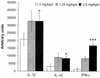
In a rat model of Borna disease, intracerebral ribavirin caused clinical improvement without changes in virus titer or nucleic acid. Levels of microglia and infiltrating CD4 and CD8 cells were decreased, despite increases in mRNAs encoding interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-10, and gamma interferon in the brain. Intracerebral ribavirin may reduce morbidity through effects on microglia cell proliferation.
Figures
References
-
- Bode, L., D. E. Dietrich, R. Stoyloff, H. M. Emrich, and H. Ludwig. 1997. Amantadine and human Borna disease virus in vitro and in vivo in an infected patient with bipolar depression. Lancet 349:178-179. - PubMed
-
- Bode, L., R. Durrwald, and H. Ludwig. 1994. Borna virus infections in cattle associated with fatal neurological disease. Vet. Rec. 135:283-284. - PubMed
-
- Bodenheimer, H. C., K. L. Lindsay, G. L. Davis, J. H. Lewis, S. N. Thung, and L. B. Seeff. 1997. Tolerance and efficacy of oral ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a multicenter trial. Hepatology 26:473-477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

