Rab proteins mediate Golgi transport of caveola-internalized glycosphingolipids and correct lipid trafficking in Niemann-Pick C cells
- PMID: 12070301
- PMCID: PMC151017
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15420
Rab proteins mediate Golgi transport of caveola-internalized glycosphingolipids and correct lipid trafficking in Niemann-Pick C cells
Abstract
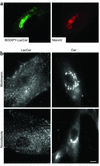
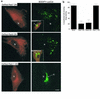
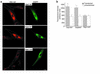
We recently showed that human skin fibroblasts internalize fluorescent analogues of the glycosphingolipids lactosylceramide and globoside almost exclusively by a clathrin-independent mechanism involving caveolae. In contrast, a sphingomyelin analogue is internalized approximately equally via clathrin-dependent and caveolar routes. Here, we further characterized the caveolar pathway for glycosphingolipids, showing that Golgi targeting of sphingolipids internalized via caveolae required microtubules and phosphoinositol 3-kinases and was inhibited in cells expressing dominant-negative Rab7 and Rab9 constructs. In addition, overexpression of wild-type Rab7 or Rab9 (but not Rab11) in Niemann-Pick type C (NP-C) lipid storage disease fibroblasts resulted in correction of lipid trafficking defects, including restoration of Golgi targeting of fluorescent lactosylceramide and endogenous GM(1) ganglioside, and a dramatic reduction in intracellular cholesterol stores. Our results demonstrate a role for Rab7 and Rab9 in the Golgi targeting of glycosphingolipids and suggest a new therapeutic approach for restoring normal lipid trafficking in NP-C cells.
Figures



References
-
- Kolesnick RN, Goni FM, Alonso A. Compartmentalization of ceramide signaling: physical foundations and biological effects. J Cell Physiol. 2000;184:285–300. - PubMed
-
- van Meer G, Holthuis JC. Sphingolipid transport in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000; 1486:145–170. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, London E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17221–17224. - PubMed
-
- Hoekstra D, van IJzendoorn SC. Lipid trafficking and sorting: how cholesterol is filling gaps. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12:496–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

