Liquid-liquid separation in solutions of normal and sickle cell hemoglobin
- PMID: 12070342
- PMCID: PMC124280
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122055299
Liquid-liquid separation in solutions of normal and sickle cell hemoglobin
Abstract
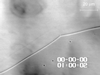
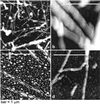
We show that in solutions of human hemoglobin (Hb)--oxy- and deoxy-Hb A or S--of near-physiological pH, ionic strength, and Hb concentration, liquid-liquid phase separation occurs reversibly and reproducibly at temperatures between 35 and 40 degrees C. In solutions of deoxy-HbS, we demonstrate that the dense liquid droplets facilitate the nucleation of HbS polymers, whose formation is the primary pathogenic event for sickle cell anemia. In view of recent results that shifts of the liquid-liquid separation phase boundary can be achieved by nontoxic additives at molar concentrations up to 30 times lower than the protein concentrations, these findings open new avenues for the inhibition of the HbS polymerization.
Figures



References
-
- Steinberg M H, Forget B G, Higgs D R, Nagel R L. Disorders of Hemoglobin: Genetics, Pathology, Clinical Management. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press; 2000.
-
- Cole-Strauss A, Yoon K, Xiang Y, Byrne B C, Rice M C, Crynn J, Holloman W K, Kmiec E B. Science. 1996;273:1386–1389. - PubMed
-
- Hahn E V, Gillespie E B. Arch Int Med. 1927;39:233–254.
-
- Sunshine H R, Hofrichter J, Ferrone F A, Eaton W A. J Mol Biol. 1982;158:251–273. - PubMed
-
- Eaton W A, Hofrichter J. In: Advances in Protein Chemistry. Anfinsen C B, Edsal J T, Richards F M, Eisenberg D S, editors. Vol. 40. San Diego: Academic; 1990. pp. 63–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

