Purification and partial characterization of bacillocin 490, a novel bacteriocin produced by a thermophilic strain of Bacillus licheniformis
- PMID: 12076356
- PMCID: PMC115367
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-1-1
Purification and partial characterization of bacillocin 490, a novel bacteriocin produced by a thermophilic strain of Bacillus licheniformis
Abstract
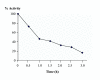
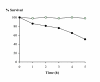
BACKGROUND: Applications of bacteriocins as food preservatives have been so far limited, principally because of their low antimicrobial activity in foods. Nisin is the only bacteriocin of significant use, but applications are restricted principally because of its very low activity at neutral or alkaline pH. Thus the isolation of new bacteriocins active in foods is desirable. RESULTS: We isolated a Bacillus licheniformis thermophilic strain producing a bacteriocin with some novel features, named here bacillocin 490. This bacteriocin was inactivated by pronase E and proteinase K and was active against closely related Bacillus spp. both in aerobic and in anaerobic conditions. Bactericidal activity was kept during storage at 4 degrees C and was remarkably stable in a wide pH range. The bacteriocin was partially purified by elution after adhesion to cells of the food-isolated strain Bacillus smithii and had a rather low mass (2 KDa). Antimicrobial activity against B. smithii was observed also when this organism was grown in water buffalo milk. CONCLUSIONS: Bacillocin 490 is a novel candidate as a food anti-microbial agent since it displays its activity in milk, is stable to heat treatment and during storage, is active in a wide pH range and has bactericidal activity also at high temperature. These features may allow the use of bacillocin 490 during processes performed at high temperature and as a complementary antimicrobial agent of nisin against some Bacillus spp. in non-acidic foods. The small size suggests its use on solid foods.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel antilisterial bacteriocin licheniocin 50.2 from Bacillus licheniformis VPS50.2 isolated from soil sample.J Appl Microbiol. 2014 Mar;116(3):502-10. doi: 10.1111/jam.12393. Epub 2013 Dec 3. J Appl Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24238327
-
Thermostable Bacteriocin BL8 from Bacillus licheniformis isolated from marine sediment.J Appl Microbiol. 2013 Mar;114(3):688-94. doi: 10.1111/jam.12097. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Appl Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23216587
-
Production and characterization of a low-molecular-weight bacteriocin from Bacillus licheniformis MKU3.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008 Dec;47(6):600-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02473.x. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19120933
-
Bacteriocin Production by Bacillus Species: Isolation, Characterization, and Application.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022 Dec;14(6):1151-1169. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09966-w. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022. PMID: 35881232 Review.
-
Recipe for Success: Suggestions and Recommendations for the Isolation and Characterisation of Bacteriocins.Int J Microbiol. 2021 Jun 17;2021:9990635. doi: 10.1155/2021/9990635. eCollection 2021. Int J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34257667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of Industrial Waste for the Production of Bio-Preservative from Bacillus licheniformis Me1 and Its Application in Milk and Milk-Based Food Products.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018 Jun;10(2):228-235. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9319-1. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018. PMID: 28842843
-
Disruption of microbial biofilms by an extracellular protein isolated from epibiotic tropical marine strain of Bacillus licheniformis.PLoS One. 2013 May 15;8(5):e64501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064501. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691235 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into Cockroach Control: Using Functional Diversity of Blattella germanica Symbionts.Insects. 2020 Oct 13;11(10):696. doi: 10.3390/insects11100696. Insects. 2020. PMID: 33066069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodiversity and antimicrobial potential of bacterial endophytes from halophyte Salicornia brachiata.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021 May;114(5):591-608. doi: 10.1007/s10482-021-01544-4. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021. PMID: 33674993
-
Cloning and characterization of mersacidin like bacteriocin from Bacillus licheniformis MKU3 in Escherichia coli.J Food Sci Technol. 2016 May;53(5):2298-306. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2195-y. Epub 2016 May 27. J Food Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27407196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klaenhammer TR. Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Biochimie. 1988;70:337–349. - PubMed
-
- Klaenhammer TR. Genetics of bacteriocins produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993;12:39–86. - PubMed
-
- Gould G. Industry perspectives on the use of natural antimicrobial and inhibitors for food applications. J Food Prot. 1996. pp. 82–86. - PubMed
-
- Favret ME, Yousten AA. Thuricin: the bacteriocin produced by Bacillus thuringensis. J Invertebr Pathol. 1989;53:206–216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

