Hepatoprotection with tauroursodeoxycholate and beta muricholate against taurolithocholate induced cholestasis: involvement of signal transduction pathways
- PMID: 12077103
- PMCID: PMC1773293
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.1.113
Hepatoprotection with tauroursodeoxycholate and beta muricholate against taurolithocholate induced cholestasis: involvement of signal transduction pathways
Abstract
Background: Tauroursodeoxycholate (TUDC) provides partial protection against taurolithocholate (TLC) induced cholestasis, possibly by inducing a signalling cascade activating protein kinase C (PKC). The potential protective effects of beta muricholic acid (beta-MC), another 7-beta-hydroxylated bile salt, have not previously been studied in TLC cholestasis.
Aims: To study the effect of beta-MC on TLC induced cholestasis and also to investigate further the effects of agents affecting intracellular signalling, notably DBcAMP (a cell permeable cAMP analogue) and several protein kinase inhibitors.
Methods: Functional studies were carried out analysing the proportion of hepatocyte couplets able to accumulate the fluorescent bile acid analogue cholyl-lysyl-fluorescein (CLF) into their sealed canalicular vacuole (cVA of CLF assay).
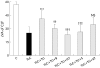
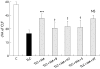
Results: It was found that both beta-MC and DBcAMP were as effective as TUDC in protecting against TLC induced cholestasis. The PKC inhibitors staurosporin and H7 but not the specific protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor KT5720 abolished the protective effects of TUDC and beta-MC. BAPTA/AM, a chelator of intracellular Ca(2+), significantly decreased the protective effect of both bile salts, and that of DBcAMP. PKC and PKA inhibitors had no effect on protection with DBcAMP.
Conclusions: Beta-MC was as effective as TUDC in protecting against TLC cholestasis. Mobilisation of Ca(2+) and activation of PKC, but not of PKA, are involved in the anticholestatic effect of the two 7-beta-hydroxylated bile salts. The hepatoprotective effects of DBcAMP involved Ca(2+) mobilisation, but not PKC or PKA activation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vasopressin-induced disruption of actin cytoskeletal organization and canalicular function in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets: possible involvement of protein kinase C.Hepatology. 1998 Oct;28(4):1031-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280418. Hepatology. 1998. PMID: 9755240
-
The protein kinase inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinylsulfonyl)-2-methyl-piperzine (H-7) prevents and reverses Ca(2+)-mediated injury in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999 Dec 1;161(2):192-201. doi: 10.1006/taap.1999.8801. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10581213
-
Silibinin prevents cholestasis-associated retrieval of the bile salt export pump, Bsep, in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets: possible involvement of cAMP.Biochem Pharmacol. 2005 Apr 1;69(7):1113-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.01.009. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15763547
-
Mechanisms of Tauroursodeoxycholate-Mediated Hepatoprotection.Dig Dis. 2017;35(3):224-231. doi: 10.1159/000450915. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Dig Dis. 2017. PMID: 28249278 Review.
-
Silymarin as a new hepatoprotective agent in experimental cholestasis: new possibilities for an ancient medication.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(9):1055-74. doi: 10.2174/092986706776360950. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16611084 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-response effect of berberine on bile acid profile and gut microbiota in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Oct 18;16(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1367-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27756364 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesoid X receptor is essential for normal glucose homeostasis.J Clin Invest. 2006 Apr;116(4):1102-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI25604. Epub 2006 Mar 23. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16557297 Free PMC article.
-
Structural modifications and augmented affinity for bile salts in enzymatically denatured egg white.Food Chem X. 2024 Jun 22;23:101577. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101577. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39036479 Free PMC article.
-
Role of apoptosis in the remodeling of cholestatic liver injury following release of the mechanical stress.Virchows Arch. 2003 Apr;442(4):372-80. doi: 10.1007/s00428-003-0773-7. Epub 2003 Mar 26. Virchows Arch. 2003. PMID: 12715172
-
Impaired localisation and transport function of canalicular Bsep in taurolithocholate induced cholestasis in the rat.Gut. 2003 Aug;52(8):1170-7. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.8.1170. Gut. 2003. PMID: 12865277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kitani K. The protective effect of hydrophilic bile acids on bile acid hepatotoxicity in the rat. Ital J Gastroenterol 1995;27:366–71. - PubMed
-
- Beuers U, Beuer JL, Paumgartenr G. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: potential mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications. Hepatology 1998;28:1449–53. - PubMed
-
- Kitani K, Kanai S. Tauroursodeoxycholate prevents taurocholate induced cholestasis. Life Sci 1982;30:515–23. - PubMed
-
- Kanai S, Ohta M, Kitani K, et al. Tauro β-muricholate is as effective as tauroursodeoxycholate in preventing taurochenodeoxycholate-induced liver damage in the rat. Life Sci 1990;47:2421–8. - PubMed
-
- Ohiwa T, Katagiri K, Hoshino M, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholate and tauro-beta-muricholate exert cytoprotection by reducing intrahepatic taurochenodeoxycholate content. Hepatology 1993;17:470–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
