The Dorsal Rel homology domain plays an active role in transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 12077338
- PMCID: PMC139791
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5089-5099.2002
The Dorsal Rel homology domain plays an active role in transcriptional regulation
Abstract
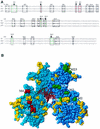
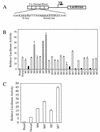
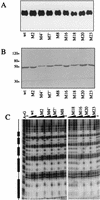
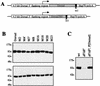
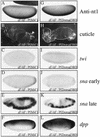
The Dorsal morphogen directs formation of the Drosophila dorsoventral axis by both activating and repressing transcription. It contains an N-terminal Rel homology domain (RHD), which is responsible for DNA binding and regulated nuclear import, and a C-terminal domain (CTD) that contains activation and repression motifs. To determine if the RHD has a direct role in transcriptional control, we analyzed a series of RHD mutations in S2 cells and embryos. Two classes of mutations (termed class I and class II mutations) that alter activation without affecting DNA binding or nuclear import were identified. The two classes appear to define distinct protein interaction surfaces on opposite faces of the RHD. Class I mutations enhance an apparently inhibitory interaction between the RHD and the CTD and eliminate both activation and repression by Dorsal. In contrast, class II mutations result in increased activation in S2 cells but severely decreased activation in embryos and have little effect on repression. Analysis of the cuticles of class II mutant embryos suggests that, in the absence of Dorsal-mediated activation, Dorsal-mediated repression is not sufficient to pattern the embryo. These results provide some of the first evidence that the RHD plays an active role in transcriptional regulation in intact multicellular organisms.
Figures

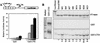

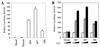
Similar articles
-
Activation and repression by the C-terminal domain of Dorsal.Development. 2001 May;128(10):1869-79. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.10.1869. Development. 2001. PMID: 11311166
-
Mutagenesis analysis of the interaction between the dorsal rel homology domain and HMG boxes of DSP1 protein.J Biochem. 2003 Oct;134(4):583-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvg177. J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14607986
-
Specificity of Rel-inhibitor interactions in Drosophila embryos.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3627-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.7.3627. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7791770 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal dynamics, spatial range, and transcriptional interpretation of the Dorsal morphogen gradient.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Dec;22(6):542-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22981910 Review.
-
Regulation of dorso/ventral patterning in the Drosophila embryo by multiple dorsal-interacting proteins.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000;33(1):1-17. doi: 10.1385/CBB:33:1:1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11322509 Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical Mechanics Metrics in Pairing and Parsing In Silico and Phenotypic Data of a Novel Genetic NFκB1 (c.T638A) Variant.Genes (Basel). 2023 Sep 24;14(10):1855. doi: 10.3390/genes14101855. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895204 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Raf Family Is a Milestone in Deciphering the Ras-Mediated Intracellular Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 5;23(9):5158. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095158. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the regulatory switches of development: lessons from enhancer evolution in Drosophila.Development. 2010 Jan;137(1):5-13. doi: 10.1242/dev.036160. Development. 2010. PMID: 20023155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NF-κB-HE4 axis: A novel regulator of HE4 secretion in ovarian cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0314564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314564. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621651 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of NFAT5 in Immune Response and Antioxidant Defense in the Thick-Shelled Mussel (Mytilus coruscus).Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;15(5):726. doi: 10.3390/ani15050726. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40076009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akimaru, H., D. X. Hou, and S. Ishii. 1997. Drosophila CBP is required for dorsal-dependent twist gene expression. Nat. Genet. 17:211-214. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, K. V., and C. Nusslein-Volhard. 1986. Dorsal-group genes of Drosophila, p. 177-194. In J. Gall (ed.), Gametogenesis and the early embryo. A. R. Liss, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bhaskar, V., S. A. Valentine, and A. J. Courey. 2000. A functional interaction between dorsal and components of the Smt3 conjugation machinery. J. Biol. Chem. 275:4033-4040. - PubMed
-
- Biehs, B., V. Francois, and E. Bier. 1996. The Drosophila short gastrulation gene prevents Dpp from autoactivating and suppressing neurogenesis in the neuroectoderm. Genes Dev. 10:2922-2934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
