Mammalian PRP4 kinase copurifies and interacts with components of both the U5 snRNP and the N-CoR deacetylase complexes
- PMID: 12077342
- PMCID: PMC139773
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5141-5156.2002
Mammalian PRP4 kinase copurifies and interacts with components of both the U5 snRNP and the N-CoR deacetylase complexes
Abstract
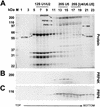
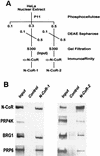
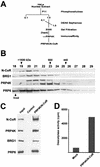
A growing body of evidence supports the coordination of pre-mRNA processing and transcriptional regulation. We demonstrate here that mammalian PRP4 kinase (PRP4K) is associated with complexes involved in both of these processes. PRP4K is implicated in pre-mRNA splicing as the homologue of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe pre-mRNA splicing kinase Prp4p, and it is enriched in SC35-containing nuclear splicing speckles. RNA interference of Caenorhabditis elegans PRP4K indicates that it is essential in metazoans. In support of a role for PRP4K in pre-mRNA splicing, we identified PRP6, SWAP, and pinin as interacting proteins and demonstrated that PRP4K is a U5 snRNP-associated kinase. In addition, BRG1 and N-CoR, components of nuclear hormone coactivator and corepressor complexes, also interact with PRP4K. PRP4K coimmunoprecipitates with N-CoR, BRG1, pinin, and PRP6, and we present data suggesting that PRP6 and BRG1 are substrates of this kinase. Lastly, PRP4K, BRG1, and PRP6 can be purified as components of the N-CoR-2 complex, and affinity-purified PRP4K/N-CoR complexes exhibit deacetylase activity. We suggest that PRP4K is an essential kinase that, in association with the both U5 snRNP and N-CoR deacetylase complexes, demonstrates a possible coordination of pre-mRNA splicing with chromatin remodeling events involved in transcriptional regulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of human genes encoding Hprp3p and Hprp4p, interacting components of the spliceosome.Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Nov;6(12):2117-26. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.12.2117. Hum Mol Genet. 1997. PMID: 9328476
-
Human PRP4 kinase is required for stable tri-snRNP association during spliceosomal B complex formation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Feb;17(2):216-21. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1718. Epub 2010 Jan 31. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20118938
-
Functional analysis of the fission yeast Prp4 protein kinase involved in pre-mRNA splicing and isolation of a putative mammalian homologue.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Mar 1;25(5):1028-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.1028. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9102632 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple genetic and biochemical interactions of Brr2, Prp8, Prp31, Prp1 and Prp4 kinase suggest a function in the control of the activation of spliceosomes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Curr Genet. 2005 Sep;48(3):151-61. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0013-6. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Curr Genet. 2005. PMID: 16133344 Review.
-
N-CoR-HDAC corepressor complexes: roles in transcriptional regulation by nuclear hormone receptors.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;274:237-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55747-7_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12596910 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of in vivo-assembled pre-mRNA splicing complexes expands the catalog of participating factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):3928-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm347. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537823 Free PMC article.
-
Spliceosome factors target timeless (tim) mRNA to control clock protein accumulation and circadian behavior in Drosophila.Elife. 2018 Dec 5;7:e39821. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39821. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30516472 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinases of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: the kinome of a divergent eukaryote.BMC Genomics. 2004 Oct 12;5:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-79. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15479470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A subset of human 35S U5 proteins, including Prp19, function prior to catalytic step 1 of splicing.EMBO J. 2004 Jun 16;23(12):2381-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600241. Epub 2004 Jun 3. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15175653 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficient tumor suppressor PRP4K is negatively regulated during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.FASEB J. 2021 Nov;35(11):e22001. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001063R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34674320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland, R., A. F. Stewart, and T. Gibson. 1996. The SANT domain: a putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21:87-88. - PubMed
-
- Bauren, G., and L. Wieslander. 1994. Splicing of Balbiani ring 1 gene pre-mRNA occurs simultaneously with transcription. Cell 76:183-192. - PubMed
-
- Brandner, J. M., S. Reidenbach, C. Kuhn, and W. W. Franke. 1998. Identification and characterization of a novel kind of nuclear protein occurring free in the nucleoplasm and in ribonucleoprotein structures of the “speckle” type. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 75:295-308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
