Generation of mice deficient for macrophage galactose- and N-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectin: limited role in lymphoid and erythroid homeostasis and evidence for multiple lectins
- PMID: 12077344
- PMCID: PMC139776
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5173-5181.2002
Generation of mice deficient for macrophage galactose- and N-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectin: limited role in lymphoid and erythroid homeostasis and evidence for multiple lectins
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol 2002 Sep;22(18):6661
Abstract
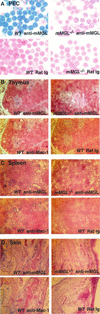
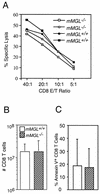
Macrophage receptors function in pattern recognition for the induction of innate immunity, in cellular communication to mediate the regulation of adaptive immune responses, and in the clearance of some glycosylated cells or glycoproteins from the circulation. They also function in homeostasis by initiating the engulfment of apoptotic cells. Evidence has suggested that macrophage receptors function to recognize cells that are destined for programmed cell death but not yet overtly apoptotic. We have examined the function of a macrophage receptor specific for unsialylated glycoproteins, known as the mouse macrophage galactose- and N-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectin (mMGL) (Ii et al., J. Biol. Chem. 265:11295-11298, 1990; Sato et al., J. Biochem. [Tokyo] 111:331-336, 1992; Yamamoto et al., Biochemistry 33:8159-8166, 1994). With targeted disruption, we tested whether mMGL is necessary for macrophage function, controlled thymic development, the loss of activated CD8 T cells, and the turnover of red blood cells. Evidence indicates that mMGL may play a nonessential role in several of these macrophage functions. Experiments are presented that indicate the existence of another galactose- and N-acetylgalactosamine-recognizing lectin distinct from mMGL. This may explain the absence of a strong phenotype in mMGL-deficient mice.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectin on mouse tumoricidal macrophages.J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):331-6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123758. J Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1587794
-
Restricted expression of galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine-specific macrophage C-type lectin to connective tissue and to metastatic lesions in mouse lung.Immunology. 1995 Dec;86(4):591-8. Immunology. 1995. PMID: 8567026 Free PMC article.
-
Initial steps in lymph node metastasis formation in an experimental system: possible involvement of recognition by macrophage C-type lectins.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2000 Apr;49(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s002620050021. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2000. PMID: 10782861 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the immunomodulatory role of the dendritic cell and macrophage-expressed C-type lectin MGL.Immunobiology. 2015 Feb;220(2):185-92. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Immunobiology. 2015. PMID: 25454488 Review.
-
The mannose receptor and other macrophage lectins.Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(1):49-52. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90123-v. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1317711 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage galactose-type lectin (MGL) is induced on M2 microglia and participates in the resolution phase of autoimmune neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jun 27;16(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1522-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31248427 Free PMC article.
-
PNA-binding glycans are expressed at high levels on horse mature and immature T lymphocytes and a subpopulation of B lymphocytes.Glycoconj J. 2005 Feb;22(1-2):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s10719-005-0228-2. Glycoconj J. 2005. PMID: 15864432
-
Liver-targeted antiviral peptide nanocomplexes as potential anti-HCV therapeutics.Biomaterials. 2015 Nov;70:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.08.014. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26298393 Free PMC article.
-
A phenotype survey of 36 mutant mouse strains with gene-targeted defects in glycosyltransferases or glycan-binding proteins.Glycobiology. 2013 Mar;23(3):363-80. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cws150. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Glycobiology. 2013. PMID: 23118208 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and function of macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 2 (MGL2/CD301b): efficient uptake and presentation of glycosylated antigens by dendritic cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 18;285(25):19193-204. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.113613. Epub 2010 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20304916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ault, K. A., and C. Knowles. 1995. In vivo biotinylation demonstrates that reticulated platelets are the youngest platelets in circulation. Exp. Hematol. 23:996-1001. - PubMed
-
- Balduini, C. L., F. Sinigaglia, E. Ascari, and C. Balduini. 1978. Behaviour of young and old desialylated rabbit erythrocytes in vivo. Hoppe Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. 359:1573-1577. - PubMed
-
- Baum, L. G., K. Derbin, N. L. Perillo, T. Wu, M. Pang, and C. Uittenbogaart. 1996. Characterization of terminal sialic acid linkages on human thymocytes. Correlation between lectin-binding phenotype and sialyltransferase expression. J. Biol. Chem. 271:10793-10799. - PubMed
-
- Bocci, V. 1981. Determinants of erythrocyte ageing: a reappraisal. Br. J. Haematol. 48:515-522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
