Association of DNA polymerase mu (pol mu) with Ku and ligase IV: role for pol mu in end-joining double-strand break repair
- PMID: 12077346
- PMCID: PMC139779
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5194-5202.2002
Association of DNA polymerase mu (pol mu) with Ku and ligase IV: role for pol mu in end-joining double-strand break repair
Abstract
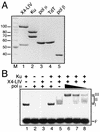
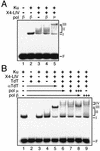
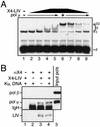
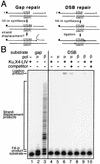
Mammalian DNA polymerase mu (pol mu) is related to terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, but its biological role is not yet clear. We show here that after exposure of cells to ionizing radiation (IR), levels of pol mu protein increase. pol mu also forms discrete nuclear foci after IR, and these foci are largely coincident with IR-induced foci of gammaH2AX, a previously characterized marker of sites of DNA double-strand breaks. pol mu is thus part of the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. pol mu also associates in cell extracts with the nonhomologous end-joining repair factor Ku and requires both Ku and another end-joining factor, XRCC4-ligase IV, to form a stable complex on DNA in vitro. pol mu in turn facilitates both stable recruitment of XRCC4-ligase IV to Ku-bound DNA and ligase IV-dependent end joining. In contrast, the related mammalian DNA polymerase beta does not form a complex with Ku and XRCC4-ligase IV and is less effective than pol mu in facilitating joining mediated by these factors. Our data thus support an important role for pol mu in the end-joining pathway for repair of double-strand breaks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A biochemically defined system for mammalian nonhomologous DNA end joining.Mol Cell. 2004 Dec 3;16(5):701-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.017. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15574326
-
Ku recruits the XRCC4-ligase IV complex to DNA ends.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(9):2996-3003. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.9.2996-3003.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10757784 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated assembly of Ku and p460 subunits of the DNA-dependent protein kinase on DNA ends is necessary for XRCC4-ligase IV recruitment.J Mol Biol. 2003 Feb 7;326(1):93-103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01328-1. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12547193
-
Mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair and chromosome aberration formation.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;104(1-4):14-20. doi: 10.1159/000077461. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15162010 Review.
-
DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Aug;44:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 14. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27264557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase requires KU80 and XRCC4 to promote N-addition at non-V(D)J chromosomal breaks in non-lymphoid cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8381-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks585. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22740656 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-apoptotic protein BCL2 down-regulates DNA end joining in cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32657-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140350. Epub 2010 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20699221 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Pleurodeles waltl DNA polymerase mu expression by extreme conditions encountered during spaceflight.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 31;8(7):e69647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069647. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936065 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Ligase D preternary-precatalytic complex performs efficient abasic sites processing at double strand breaks during nonhomologous end joining.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jun 4;47(10):5276-5292. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz265. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30976810 Free PMC article.
-
The minimal Bacillus subtilis nonhomologous end joining repair machinery.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e64232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064232. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogue, M. A., C. Wang, C. Zhu, and D. B. Roth. 1997. V(D)J recombination in Ku86-deficient mice: distinct effects on coding, signal, and hybrid joint formation. Immunity 7:37-47. - PubMed
-
- Bross, L., Y. Fukita, F. McBlane, C. Demolliere, K. Rajewsky, and H. Jacobs. 2000. DNA double-strand breaks in immunoglobulin genes undergoing somatic hypermutation. Immunity 13:589-597. - PubMed
-
- Chen, S., K. V. Inamdar, P. Pfeiffer, E. Feldmann, M. F. Hannah, Y. Yu, J. W. Lee, T. Zhou, S. P. Lees-Miller, and L. F. Povirk. 2001. Accurate in vitro end joining of a DNA double strand break with partially cohesive 3′-overhangs and 3′-phosphoglycolate termini: effect of Ku on repair fidelity. J. Biol. Chem. 276:24323-24330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
