Pancreas and islet cell transplantation
- PMID: 12079269
- PMCID: PMC3184836
- DOI: 10.1053/bega.2002.0318
Pancreas and islet cell transplantation
Abstract
Currently, for the patient with type 1 diabetes, a definitive treatment without resorting to the use of exogenous insulin can be achieved only with pancreas or islet cell transplantation. These means of restoring beta-cell mass can completely maintain essentially normal long-term glucose homeostasis, although the need for powerful immunosuppressive regimens limits their application to only a subgroup of adult patients. Apart from the shortage of donors that has limited all kinds of transplantation, however, the widespread use of beta-cell replacement has been precluded until recently by the drawbacks associated with both organ and islet cell transplantation. Although the study of recurrence of diabetes has generated attention, the fundamental obstacle to pancreas and islet transplantation has been, and remains, the alloimmune response. With a better elucidation of the mechanisms of alloengraftment achieved during the last 3 years, the stage has been set for further advances.
Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science Ltd.
Figures
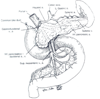
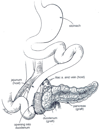
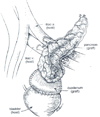


Similar articles
-
[End-stage nephropathy in type 1-diabetes mellitus - kidney transplantation alone or combined with islet or pancreas transplantation?].Ther Umsch. 2011 Dec;68(12):699-706. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930/a000233. Ther Umsch. 2011. PMID: 22139985 Review. German.
-
Pancreas-After-Islet Transplantation in Nonuremic Type 1 Diabetes: A Strategy for Restoring Durable Insulin Independence.Am J Transplant. 2017 Sep;17(9):2444-2450. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14344. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Am J Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28489277 Free PMC article.
-
[Treatment of type 1 diabetics by transplantation of isolated pancreatic islets].Rinsho Byori. 2006 Apr;54(4):379-85. Rinsho Byori. 2006. PMID: 16722457 Japanese.
-
Beta-cell replacement for type I diabetes.Annu Rev Med. 2004;55:133-56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.55.091902.103539. Annu Rev Med. 2004. PMID: 14746513 Review.
-
[Islet cell and pancreas transplantation in diabetes: status 1996].Ther Umsch. 1996 Dec;53(12):889-901. Ther Umsch. 1996. PMID: 9036567 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Hyperinsulinaemia and hyperglycaemia: possible risk factors of colorectal cancer among diabetic patients.Diabetologia. 2003 May;46(5):595-607. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1109-5. Epub 2003 May 23. Diabetologia. 2003. PMID: 12764580 Review.
-
Facilitating physiologic self-regeneration: a step beyond islet cell replacement.Pharm Res. 2006 Feb;23(2):227-42. doi: 10.1007/s11095-005-9095-6. Epub 2006 Jan 1. Pharm Res. 2006. PMID: 16323065 Review.
-
Current status and prospects for gene and cell therapeutics for type 1 diabetes mellitus.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2003 Dec;4(4):369-80. doi: 10.1023/a:1027306213563. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2003. PMID: 14618022 Review. No abstract available.
-
Stem cell therapy. Use of differentiated pluripotent stem cells as replacement therapy for treating disease.Science. 2014 Aug 22;345(6199):1247391. doi: 10.1126/science.1247391. Science. 2014. PMID: 25146295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Matrix and Integrins in Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation.Biochem Insights. 2015 Sep 28;8(Suppl 2):15-21. doi: 10.4137/BCI.S30377. eCollection 2015. Biochem Insights. 2015. PMID: 26462244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Report of a WHO Consultation. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications.
-
- Amos AF, McCarthy DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabetes Medicine. 1997;14 supplement 5:S1–S85. - PubMed
-
- Harris MI. Diabetes in America: epidemiology and scope of the problem. Diabetes Care. 1998;21 supplement 3:C11–C14. - PubMed
-
- Bjork S. The cost of diabetes and diabetes care. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2001;54 supplement 1:S13–S18. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(1S):5OS–53S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

