Autoantibodies against interleukin 1alpha in rheumatoid arthritis: association with long term radiographic outcome
- PMID: 12079899
- PMCID: PMC1754172
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.61.7.598
Autoantibodies against interleukin 1alpha in rheumatoid arthritis: association with long term radiographic outcome
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the possible association of interleukin 1alpha autoantibodies (IL1alpha aAb) with the long term course of joint erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Serum samples from 176 patients with RA included in a prospective study over 30 years were analysed for IL1alpha aAb by binding to human [(125)I]IL1alpha. Erosions of 19 diarthrodial joints were radiographically scored by the Larsen method.
Results: The relative risk (RR) of early IL1alpha aAb positive patients developing at least 30% of maximum radiographic joint destruction was significantly lower than for IL1alpha aAb negative patients, RR=0.29 (p=0.04). In rheumatoid factor positive patients RR was only 0.18 (p=0.02). Patients who seroconverted more than two years after the onset of RA showed the most aggressive development of joint erosion, with a relative risk of at least 40% of maximum radiographic joint destruction of 2.56 (p=0.048)
Conclusions: The progression of radiographic joint destruction in patients with RA is associated with, and perhaps modified by, circulating IL1alpha aAb, suggesting that IL1alpha or IL1alpha aAb, or both, have a role in the erosive processes. IL1alpha aAb appear to be of prognostic significance in RA.
Figures
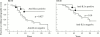
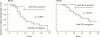
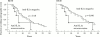
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

