Neurogenin 3 is essential for the proper specification of gastric enteroendocrine cells and the maintenance of gastric epithelial cell identity
- PMID: 12080087
- PMCID: PMC186338
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.985002
Neurogenin 3 is essential for the proper specification of gastric enteroendocrine cells and the maintenance of gastric epithelial cell identity
Abstract
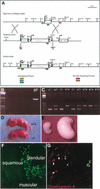
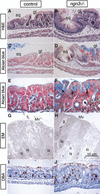
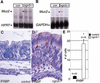
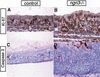
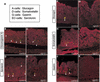
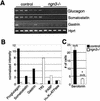
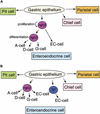
The notch signaling pathway is essential for the endocrine cell fate in various tissues including the enteroendocrine system of the gastrointestinal tract. Enteroendocrine cells are one of the four major cell types found in the gastric epithelium of the glandular stomach. To understand the molecular basis of enteroendocrine cell development, we have used gene targeting in mouse embryonic stem cells to derive an EGFP-marked null allele of the bHLH transcription factor, neurogenin 3 (ngn3). In ngn3(-/-) mice, glucagon secreting A-cells, somatostatin secreting D-cells, and gastrin secreting G-cells are absent from the epithelium of the glandular stomach, whereas the number of serotonin-expressing enterochromaffin (EC) cells is decreased dramatically. In addition, ngn3(-/-) mice display intestinal metaplasia of the gastric epithelium. Thus, ngn3 is required for the differentiation of enteroendocrine cells in the stomach and the maintenance of gastric epithelial cell identity.
Figures
References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JF. Extracellular matrix components and integrins in relationship to human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1997;31:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Borges M, Linnoila RI, van de Velde HJ, Chen H, Nelkin BD, Mabry M, Baylin SB, Ball DW. An achaete-scute homologue essential for neuroendocrine differentiation in the lung. Nature. 1997;386:852–855. - PubMed
-
- Duncan SA, Nagy A, Chan W. Murine gastrulation requires HNF-4 regulated gene expression in the visceral endoderm: Tetraploid rescue of Hnf-4(−/−) embryos. Development. 1997;124:279–287. - PubMed
-
- Falk P, Roth KA, Gordon JI. Lectins are sensitive tools for defining the differentiation programs of mouse gut epithelial cell lineages. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:G987–G1003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
