Lysine methylation within the globular domain of histone H3 by Dot1 is important for telomeric silencing and Sir protein association
- PMID: 12080090
- PMCID: PMC186335
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1001502
Lysine methylation within the globular domain of histone H3 by Dot1 is important for telomeric silencing and Sir protein association
Abstract
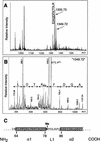
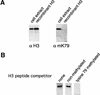
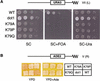
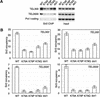
The amino-terminal histone tails are subject to covalent post-translational modifications such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation. In the histone code hypothesis, these exposed and unstructured histone tails are accessible to a repertoire of regulatory factors that specifically recognize the various modified histones, thereby generating altered chromatin structures that mediate specific biological responses. Here, we report that lysine (Lys) 79 of histone H3, which resides in the globular domain, is methylated in eukaryotic organisms. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lys 79 of histone H3 is methylated by Dot1, a protein shown previously to play a role in telomeric silencing. Mutations of Lys 79 of histone H3 and mutations that abolish the catalytic activity of Dot1 impair telomeric silencing, suggesting that Dot1 mediates telomeric silencing largely through methylation of Lys 79. This defect in telomeric silencing might reflect an interaction between Sir proteins and Lys 79, because dot1 and Lys 79 mutations weaken the interaction of Sir2 and Sir3 with the telomeric region in vivo. Our results indicate that histone modifications in the core globular domain have important biological functions.
Figures



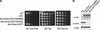

References
-
- Aparicio OM, Billington BL, Gottschling DE. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991;66:1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Boggs BA, Cheung P, Heard E, Spector DL, Chinault AC, Allis CD. Differentially methylated forms of histone H3 show unique association patterns with inactive human X chromosomes. Nat Genet. 2002;30:73–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
