The bacteriophage T4 transcription activator MotA interacts with the far-C-terminal region of the sigma70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
- PMID: 12081968
- PMCID: PMC135182
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.14.3957-3964.2002
The bacteriophage T4 transcription activator MotA interacts with the far-C-terminal region of the sigma70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
Abstract
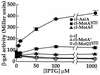
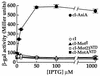
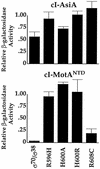
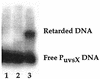
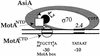
Transcription from bacteriophage T4 middle promoters uses Escherichia coli RNA polymerase together with the T4 transcriptional activator MotA and the T4 coactivator AsiA. AsiA binds tightly within the C-terminal portion of the sigma70 subunit of RNA polymerase, while MotA binds to the 9-bp MotA box motif, which is centered at -30, and also interacts with sigma70. We show here that the N-terminal half of MotA (MotA(NTD)), which is thought to include the activation domain, interacts with the C-terminal region of sigma70 in an E. coli two-hybrid assay. Replacement of the C-terminal 17 residues of sigma70 with comparable sigma38 residues abolishes the interaction with MotA(NTD) in this assay, as does the introduction of the amino acid substitution R608C. Furthermore, in vitro transcription experiments indicate that a polymerase reconstituted with a sigma70 that lacks C-terminal amino acids 604 to 613 or 608 to 613 is defective for MotA-dependent activation. We also show that a proteolyzed fragment of MotA that contains the C-terminal half (MotA(CTD)) binds DNA with a K(D(app)) that is similar to that of full-length MotA. Our results support a model for MotA-dependent activation in which protein-protein contact between DNA-bound MotA and the far-C-terminal region of sigma70 helps to substitute functionally for an interaction between sigma70 and a promoter -35 element.
Figures


References
-
- Brody, E., D. Rabussay, and D. Hall. 1983. Regulation of transcription of prereplicative genes, p. 174-183. In C. K. Mathews, E. M. Kutter, G. Mosig, and P. B. Berget (ed.), Bacteriophage T4. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Busby, S., and R. Ebright. 1999. Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP). J. Mol. Biol. 293:199-213. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, E. A., O. Muzzin, M. Chlenov, J. L. Sun, C. A. Olson, O. Weinman, M. L. Trester-Zedlitz, and S. A. Darst. 2002. Structure of the bacterial RNA polymerase promoter specificity sigma subunit. Mol. Cell 9:527-539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

