The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1 in regulating the destruction of cyclin B in space and time
- PMID: 12082076
- PMCID: PMC2173543
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200203035
The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1 in regulating the destruction of cyclin B in space and time
Abstract
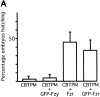
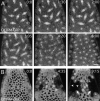
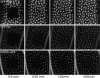
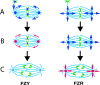
In Drosophila cells cyclin B is normally degraded in two phases: (a) destruction of the spindle-associated cyclin B initiates at centrosomes and spreads to the spindle equator; and (b) any remaining cytoplasmic cyclin B is degraded slightly later in mitosis. We show that the APC/C regulators Fizzy (Fzy)/Cdc20 and Fzy-related (Fzr)/Cdh1 bind to microtubules in vitro and associate with spindles in vivo. Fzy/Cdc20 is concentrated at kinetochores and centrosomes early in mitosis, whereas Fzr/Cdh1 is concentrated at centrosomes throughout the cell cycle. In syncytial embryos, only Fzy/Cdc20 is present, and only the spindle-associated cyclin B is degraded at the end of mitosis. A destruction box-mutated form of cyclin B (cyclin B triple-point mutant [CBTPM]-GFP) that cannot be targeted for destruction by Fzy/Cdc20, is no longer degraded on spindles in syncytial embryos. However, CBTPM-GFP can be targeted for destruction by Fzr/Cdh1. In cellularized embryos, which normally express Fzr/Cdh1, CBTPM-GFP is degraded throughout the cell but with slowed kinetics. These findings suggest that Fzy/Cdc20 is responsible for catalyzing the first phase of cyclin B destruction that occurs on the mitotic spindle, whereas Fzr/Cdh1 is responsible for catalyzing the second phase of cyclin B destruction that occurs throughout the cell. These observations have important implications for the mechanisms of the spindle checkpoint.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Timing of APC/C substrate degradation is determined by fzy/fzr specificity of destruction boxes.EMBO J. 2002 Sep 2;21(17):4500-10. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf452. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12198152 Free PMC article.
-
Completion of mitosis requires neither fzr/rap nor fzr2, a male germline-specific Drosophila Cdh1 homolog.Curr Biol. 2002 Aug 20;12(16):1435-41. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01074-6. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12194827
-
The Cdc20 (Fzy)/Cdh1-related protein, Cort, cooperates with Fzy in cyclin destruction and anaphase progression in meiosis I and II in Drosophila.Development. 2007 Mar;134(5):891-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.02784. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Development. 2007. PMID: 17251266 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin destruction in mitosis: a crucial task of Cdc20.FEBS Lett. 2002 Dec 4;532(1-2):7-11. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03657-8. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12459453 Review.
-
Cyclin A and Nek2A: APC/C-Cdc20 substrates invisible to the mitotic spindle checkpoint.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):72-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380072. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074038 Review.
Cited by
-
Human KIAA1018/FAN1 nuclease is a new mitotic substrate of APC/C(Cdh1).Chin J Cancer. 2012 Sep;31(9):440-8. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10144. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Chin J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22854063 Free PMC article.
-
Studying mitotic checkpoint by illustrating dynamic kinetochore protein behavior and chromosome motion in living Drosophila syncytial embryos.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 14;(64):e3763. doi: 10.3791/3763. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22733107 Free PMC article.
-
Fzr regulates silk gland growth by promoting endoreplication and protein synthesis in the silkworm.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jan 18;19(1):e1010602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010602. eCollection 2023 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36652497 Free PMC article.
-
Tellurium notebooks-An environment for reproducible dynamical modeling in systems biology.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Jun 15;14(6):e1006220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006220. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29906293 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of Cdc20 to the kinetochore requires BubR1 but not Mad2 in Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(13):3384-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00258-10. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20421417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrieu, A., J.A. Kahana, K.W. Wood, and D.W. Cleveland. 2000. CENP-E as an essential component of the mitotic checkpoint in vitro. Cell. 102:817–826. - PubMed
-
- Abrieu, A., L. Magnaghi-Jaulin, J.A. Kahana, M. Peter, A. Castro, S. Vigneron, T. Lorca, D.W. Cleveland, and J.C. Labbe. 2001. Mps1 is a kinetochore-associated kinase essential for the vertebrate mitotic checkpoint. Cell. 106:83–93. - PubMed
-
- Bardin, A.J., R. Visintin, and A. Amon. 2000. A mechanism for coupling exit from mitosis to partitioning of the nucleus. Cell. 102:21–31. - PubMed
-
- Basto, R., R. Gomes, and R.E. Karess. 2000. Rough deal and Zw10 are required for the metaphase checkpoint in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:939–943. - PubMed
-
- Chan, G.K., S.A. Jablonski, D.A. Starr, M.L. Goldberg, and T.J. Yen. 2000. Human Zw10 and ROD are mitotic checkpoint proteins that bind to kinetochores. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:944–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

