The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1 in regulating the destruction of cyclin B in space and time
- PMID: 12082076
- PMCID: PMC2173543
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200203035
The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1 in regulating the destruction of cyclin B in space and time
Abstract
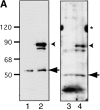
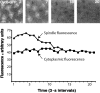
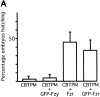
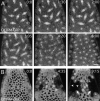
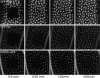
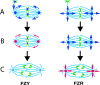
In Drosophila cells cyclin B is normally degraded in two phases: (a) destruction of the spindle-associated cyclin B initiates at centrosomes and spreads to the spindle equator; and (b) any remaining cytoplasmic cyclin B is degraded slightly later in mitosis. We show that the APC/C regulators Fizzy (Fzy)/Cdc20 and Fzy-related (Fzr)/Cdh1 bind to microtubules in vitro and associate with spindles in vivo. Fzy/Cdc20 is concentrated at kinetochores and centrosomes early in mitosis, whereas Fzr/Cdh1 is concentrated at centrosomes throughout the cell cycle. In syncytial embryos, only Fzy/Cdc20 is present, and only the spindle-associated cyclin B is degraded at the end of mitosis. A destruction box-mutated form of cyclin B (cyclin B triple-point mutant [CBTPM]-GFP) that cannot be targeted for destruction by Fzy/Cdc20, is no longer degraded on spindles in syncytial embryos. However, CBTPM-GFP can be targeted for destruction by Fzr/Cdh1. In cellularized embryos, which normally express Fzr/Cdh1, CBTPM-GFP is degraded throughout the cell but with slowed kinetics. These findings suggest that Fzy/Cdc20 is responsible for catalyzing the first phase of cyclin B destruction that occurs on the mitotic spindle, whereas Fzr/Cdh1 is responsible for catalyzing the second phase of cyclin B destruction that occurs throughout the cell. These observations have important implications for the mechanisms of the spindle checkpoint.
Figures




References
-
- Abrieu, A., J.A. Kahana, K.W. Wood, and D.W. Cleveland. 2000. CENP-E as an essential component of the mitotic checkpoint in vitro. Cell. 102:817–826. - PubMed
-
- Abrieu, A., L. Magnaghi-Jaulin, J.A. Kahana, M. Peter, A. Castro, S. Vigneron, T. Lorca, D.W. Cleveland, and J.C. Labbe. 2001. Mps1 is a kinetochore-associated kinase essential for the vertebrate mitotic checkpoint. Cell. 106:83–93. - PubMed
-
- Bardin, A.J., R. Visintin, and A. Amon. 2000. A mechanism for coupling exit from mitosis to partitioning of the nucleus. Cell. 102:21–31. - PubMed
-
- Basto, R., R. Gomes, and R.E. Karess. 2000. Rough deal and Zw10 are required for the metaphase checkpoint in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:939–943. - PubMed
-
- Chan, G.K., S.A. Jablonski, D.A. Starr, M.L. Goldberg, and T.J. Yen. 2000. Human Zw10 and ROD are mitotic checkpoint proteins that bind to kinetochores. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:944–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

