Matrix assembly, regulation, and survival functions of laminin and its receptors in embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 12082085
- PMCID: PMC2173546
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200203073
Matrix assembly, regulation, and survival functions of laminin and its receptors in embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
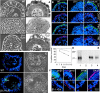
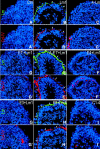
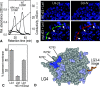
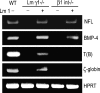
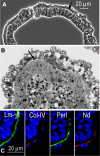
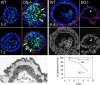
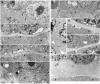
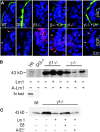
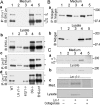
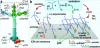
Laminin-1 is essential for early embryonic basement membrane assembly and differentiation. Several steps can be distinguished, i.e., the expression of laminin and companion matrix components, their accumulation on the cell surface and assembly into basement membrane between endoderm and inner cell mass, and the ensuing differentiation of epiblast. In this study, we used differentiating embryoid bodies derived from mouse embryonic stem cells null for gamma1-laminin, beta1-integrin and alpha/beta-dystroglycan to dissect the contributions of laminin domains and interacting receptors to this process. We found that (a) laminin enables beta1-integrin-null embryoid bodies to assemble basement membrane and achieve epiblast with beta1-integrin enabling expression of the laminin alpha1 subunit; (b) basement membrane assembly and differentiation require laminin polymerization in conjunction with cell anchorage, the latter critically dependent upon a heparin-binding locus within LG module-4; (c) dystroglycan is not uniquely required for basement membrane assembly or initial differentiation; (d) dystroglycan and integrin cooperate to sustain survival of the epiblast and regulate laminin expression; and (e) laminin, acting via beta1-integrin through LG1-3 and requiring polymerization, can regulate dystroglycan expression.
Figures
References
-
- Andac, Z., T. Sasaki, K. Mann, A. Brancaccio, R. Deutzmann, and R. Timpl. 1999. Analysis of heparin, alpha-dystroglycan and sulfatide binding to the G domain of the laminin alpha1 chain by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 287:253–264. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley, M., M. Pesch, L. Tunggal, F. Gaill, and R. Fässler. 2000. Altered synthesis of laminin 1 and absence of basement membrane component deposition in beta-1 integrin-deficient embryoid bodies. J. Cell Sci. 113:259–268. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, Y.S., M.F. Champliaud, R.E. Burgeson, M.P. Marinkovich, and P.D. Yurchenco. 1997. Self-assembly of laminin isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31525–31532. - PubMed
-
- Colognato, H., and P.D. Yurchenco. 2000. Form and function: the laminin family of heterotrimers. Dev. Dyn. 218:213–234. - PubMed
-
- Colognato, H., M. MacCarrick, J.J. O'Rear, and P.D. Yurchenco. 1997. The laminin alpha2-chain short arm mediates cell adhesion through both the alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 272:29330–29336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

