STAT6 mediates interleukin-4 growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 12082548
- PMCID: PMC1531710
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900248
STAT6 mediates interleukin-4 growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
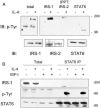
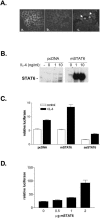
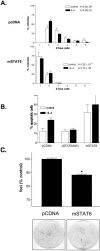
In addition to acting as a hematopoietic growth factor, interleukin-4 (IL-4) inhibits growth of some transformed cells in vitro and in vivo. In this study, we show that insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, IRS-2, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) are phosphorylated following IL-4 treatment in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. STAT6 DNA binding is enhanced by IL-4 treatment. STAT6 activation occurs even after IRS-1 depletion, suggesting the two pathways are independent. To examine the role of STAT6 in IL-4-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis, a full-length STAT6 cDNA was transfected into MCF-7 cells. Transient overexpression of STAT6 resulted in both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of the protein, increased DNA binding in response to IL-4, and increased transactivation of an IL-4 responsive promoter. In STAT6-transfected cells, basal proliferation was reduced whereas apoptosis was increased. Finally, stable expression of STAT6 resulted in reduced foci formation compared to vector-transfected cells alone. These results suggest STAT6 is required for IL-4-mediated growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple signaling pathways mediate interleukin-4-induced 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta5-delta4 isomerase type 1 gene expression in human breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Feb;14(2):229-40. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.2.0416. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10674396
-
Interleukin-4-induced transcriptional activation by stat6 involves multiple serine/threonine kinase pathways and serine phosphorylation of stat6.Blood. 2000 Jan 15;95(2):494-502. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10627454
-
Regulation of breast cancer cell motility by insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) in metastatic variants of human breast cancer cell lines.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 1;20(50):7318-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204920. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11704861
-
STAT6: its role in interleukin 4-mediated biological functions.J Mol Med (Berl). 1997 May;75(5):317-26. doi: 10.1007/s001090050117. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997. PMID: 9181473 Review.
-
The roles of post-translational modifications and coactivators of STAT6 signaling in tumor growth and progression.Future Med Chem. 2020 Nov;12(21):1945-1960. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0224. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32779479 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Functions of T Lymphocytes in Breast Carcinoma: From Immune Protection to Orchestrating Tumor Progression and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;15(19):4771. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194771. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microarray data analysis reveals gene expression changes in response to ionizing radiation in MCF7 human breast cancer cells.Hereditas. 2020 Sep 3;157(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s41065-020-00151-z. Hereditas. 2020. PMID: 32883354 Free PMC article.
-
Production of interleukin‑4 in CD133+ cervical cancer stem cells promotes resistance to apoptosis and initiates tumor growth.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):5068-76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5195. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. Retraction in: Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):4008. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5732. PMID: 27121303 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Mediated by NF-κB Factor as Prognostic Markers in Mammary Tumors.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:9512743. doi: 10.1155/2016/9512743. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 26989335 Free PMC article.
-
Selective expansion of chimeric antigen receptor-targeted T-cells with potent effector function using interleukin-4.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 13;285(33):25538-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.127951. Epub 2010 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20562098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Shami A, Naccache P. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-activated signaling pathways in human neutrophils. Involvement of Jak2 in the stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5333–5338. - PubMed
-
- Blais Y, Gingras S, Haagensen DE, Labrie F, Simard J. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 inhibit estrogen-induced breast cancer cell proliferation and stimulate GCDFP-15 expression in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1996;121:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Bonneterre J, Peyrat J, Beuscart R, Demaille A. Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor I receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6931–6935. - PubMed
-
- Chang TLY, Peng XB, Fu XY. Interleukin-4 mediates cell growth inhibition through activation of Stat1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10212–10217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
