Molecular proximity of Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels and beta(1)-integrins on the plasma membrane of melanoma cells: effects of cell adherence and channel blockers
- PMID: 12084773
- PMCID: PMC2311400
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.20028607
Molecular proximity of Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels and beta(1)-integrins on the plasma membrane of melanoma cells: effects of cell adherence and channel blockers
Abstract
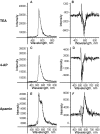
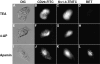
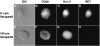
Tumor cell membranes have multiple components that participate in the process of metastasis. The present study investigates the physical association of beta1-integrins and Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels in melanoma cell membranes using resonance energy transfer (RET) techniques. RET between donor-labeled anti-beta1-integrin and acceptor-labeled anti-Kv1.3 channels was detected on LOX cells adherent to glass and fibronectin-coated coverslips. However, RET was not observed on LOX cells in suspension, indicating that molecular proximity of these membrane molecules is adherence-related. Several K(+) channel blockers, including tetraethylammonium, 4-aminopyridine, and verapamil, inhibited RET between beta1-integrins and Kv1.3 channels. However, the irrelevant K(+) channel blocker apamin had no effect on RET between beta1-integrins and Kv1.3 channels. Based on these findings, we speculate that the lateral association of Kv1.3 channels with beta1-integrins contributes to the regulation of integrin function and that channel blockers might affect tumor cell behavior by influencing the assembly of supramolecular structures containing integrins.
Figures






References
-
- Albelda, S.M. 1993. Biology of disease. Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab. Invest. 68:4–17. - PubMed
-
- Arcangeli, A., M.R. Del Bene, R. Poli, L. Ricupero, and M. Olivotto. 1989. Mutual contact of murine erythroleukemia cells activates depolarizing cation channels, whereas contact with extracellular substrata activates hyperpolarizing Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. J. Cell. Physiol. 139:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Arcangeli, A., A. Becchetti, M.R. Bene, E. Wanke, and M. Olivotto. 1991. Fibronectin-integrin binding promotes hyperpolarization of murine erythroleukemia cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 177:1266–1272. - PubMed
-
- Arcangeli, A., L. Faravelli, L. Bianchi, B. Rosati, A. Gritti, A. Vescovi, E. Wanke, and M. Olivotto. 1996. Soluble or bound laminin elicit in human neuroblastoma cells short- or long-term potentiation of a K+ inwardly rectifying current: relevance to neuritogenesis. Cell Adhes. Commun. 4:369–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

