Membrane protein transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi in tobacco leaves is energy dependent but cytoskeleton independent: evidence from selective photobleaching
- PMID: 12084828
- PMCID: PMC150781
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.001586
Membrane protein transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi in tobacco leaves is energy dependent but cytoskeleton independent: evidence from selective photobleaching
Abstract
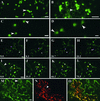
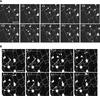
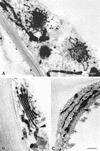
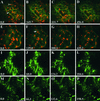
The mechanisms that control protein transport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi apparatus are poorly characterized in plants. Here, we examine in tobacco leaves the structural relationship between Golgi and ER membranes using electron microscopy and demonstrate that Golgi membranes contain elements that are in close association and/or in direct contact with the ER. We further visualized protein trafficking between the ER and the Golgi using Golgi marker proteins tagged with green fluorescent protein. Using photobleaching techniques, we showed that Golgi membrane markers constitutively cycle to and from the Golgi in an energy-dependent and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive manner. We found that membrane protein transport toward the Golgi occurs independently of the cytoskeleton and does not require the Golgi to be motile along the surface of the ER. Brefeldin A treatment blocked forward trafficking of Golgi proteins before their redistribution into the ER. Our results indicate that in plant cells, the Golgi apparatus is a dynamic membrane system whose components continuously traffic via membrane trafficking pathways regulated by brefeldin A- and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive machinery.
Figures

References
-
- Andreeva, A.V., Kutuzov, M.A., Evans, D.E., and Hawes, C.R. (1997). Rab-GDP dissociation inhibitor isoforms in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 48, 2109–2110.
-
- Andreeva, A.V., Zheng, H., Saint-Jore, C.M., Kutuzov, M.A., Evans, D.E., and Hawes, C.R. (2000). Organization of transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi in higher plant. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28, 505–512. - PubMed
-
- Aridor, M., and Balch, W.E. (2000). Kinase signaling initiates coat complex II (COPII) recruitment and export from the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35673–35676. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe, C. (2000). Traffic COPs of the early secretory pathway. Traffic 1, 371–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

