Jasmonate response locus JAR1 and several related Arabidopsis genes encode enzymes of the firefly luciferase superfamily that show activity on jasmonic, salicylic, and indole-3-acetic acids in an assay for adenylation
- PMID: 12084835
- PMCID: PMC150788
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.000885
Jasmonate response locus JAR1 and several related Arabidopsis genes encode enzymes of the firefly luciferase superfamily that show activity on jasmonic, salicylic, and indole-3-acetic acids in an assay for adenylation
Abstract
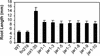
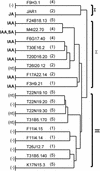
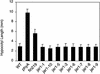
Jasmonic acid (JA) and related cyclopentanones are critical plant signaling molecules, but their mode of action at the molecular level is unclear. A map-based approach was used to identify the defective gene in the Arabidopsis JA response mutant jar1-1. JAR1 is 1 of 19 closely related Arabidopsis genes that are similar to the auxin-induced soybean GH3 gene. Analysis of fold predictions for this protein family suggested that JAR1 might belong to the acyl adenylate-forming firefly luciferase superfamily. These enzymes activate the carboxyl groups of a variety of substrates for their subsequent biochemical modification. An ATP-PPi isotope exchange assay was used to demonstrate adenylation activity in a glutathione S-transferase-JAR1 fusion protein. Activity was specific for JA, suggesting that covalent modification of JA is important for its function. Six other Arabidopsis genes were specifically active on indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), and one was active on both IAA and salicylic acid. These findings suggest that the JAR1 gene family is involved in multiple important plant signaling pathways.
Figures




References
-
- Berger, S., Bell, E., Sadka, A., and Mullet, J.E. (1995). Arabidopsis thaliana Atvsp is homologous to soybean VspA and VspB, genes encoding vegetative storage protein acid phosphatases, and is regulated similarly by methyl jasmonate, wounding, sugars, light and phosphate. Plant Mol. Biol. 27, 933–942. - PubMed
-
- Black, P.N., DiRusso, C.C., Sherin, D., MacColl, R., Knudsen, J., and Weimar, J.D. (2000). Affinity labeling fatty acyl-CoA synthetase with 9-p-azidophenoxy nonanoic acid and the identification of the fatty acid-binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 38547–38553. - PubMed
-
- Chang, K.H., Xiang, H., and Dunaway-Mariano, D. (1997). Acyl-adenylate motif of the acyl-adenylate/thioester-forming enzyme superfamily: A site-directed mutagenesis study with the Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 4-chlorobenzoate:coenzyme A ligase. Biochemistry 36, 15650–15659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

