Specificity and affinity motifs for Grb2 SH2-ligand interactions
- PMID: 12084912
- PMCID: PMC124298
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.142224499
Specificity and affinity motifs for Grb2 SH2-ligand interactions
Abstract
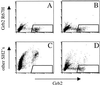
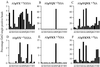
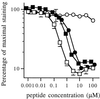
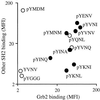
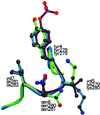
Protein-protein interactions are often mediated by the recognition of short continuous amino acid stretches on target proteins by specific binding domains. Affinity-based selection strategies have successfully been used to define recognition motifs for a large series of such protein domains. However, in many biological systems specificity of interaction may be of equal or greater importance than affinity. To address this issue we have developed a peptide library screening technology that can be used to directly define ligands for protein domains based on both affinity and specificity of interaction. We demonstrate the value of this approach by the selection of peptide ligands that are either highly specific for the Grb2 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain or that are cross-reactive between a group of related SH2 domains. Examination of previously identified physiological ligands for the Grb2 SH2 domain suggests that for these ligands regulation of the specificity of interaction may be an important factor for in vivo ligand selection.
Figures
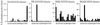

References
-
- Sudol M. Oncogene. 1998;17:1469–1474. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, Koch C A, Grey L, Ellis C, Moran M F, Pawson T. Science. 1990;250:979–982. - PubMed
-
- Songyang Z, Shoelson S E, Chaudhuri M, Gish G, Pawson T, Haser W G, King F, Roberts T, Ratnofsky S, Lechleider R J, et al. Cell. 1993;72:767–778. - PubMed
-
- Oligino L, Lung F D, Sastry L, Bigelow J, Cao T, Curran M, Burke T R, Jr, Wang S, Krag D, Roller P P, et al. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29046–29052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

