The myelin basic protein gene is expressed in differentiated blood cell lineages and in hemopoietic progenitors
- PMID: 12084930
- PMCID: PMC124388
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122079599
The myelin basic protein gene is expressed in differentiated blood cell lineages and in hemopoietic progenitors
Abstract
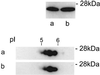
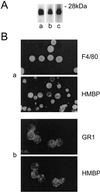
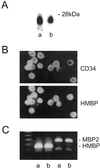
Myelin basic proteins (MBP) are major constituents of the myelin sheath of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, respectively. We previously showed that MBP-related transcripts are present in the bone marrow and the immune system. These mRNAs are transcribed from a region called 0', consisting of three exons, located upstream of the classical MBP exons; these three exons belong to the long MBP gene otherwise called "Golli-MBP." The most abundant of these mRNAs, now called HMBP (hemopoietic MBP), encompasses the sequence encoded by the region 0' plus exon 1 and part of intron 1 of the classic MBP gene. Antisera to recombinant HMBP proteins are immunoreactive with proteins of about 26-28 kDa in brain, thymus, and spleen. This report demonstrates that HMBP proteins are present in the vast majority (>95%) of thymic T cells, which express the corresponding transcripts, as do mature T cells from lymph nodes and spleen. HMBP mRNAs and proteins are also manifest in the majority of spleen B lymphocytes and in B cell lines. In addition to lymphoid cells, HMBP proteins are in all types of myeloid lineage cells, i.e., macrophages, dendritic cells, and granulocytes, as well as in megakaryocytes and erythroblasts. Finally, HMBP proteins are present in CD34+ bone marrow cells, and, furthermore, in highly proliferative cultures, these CD34+ cells express HMBP RNAs and proteins. Thus, MBP gene products are present both in the nervous system and in the entire hemopoietic system.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel transcript overlapping the myelin basic protein gene.J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):2318-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10126.x. J Neurochem. 1992. PMID: 1279125
-
The human myelin basic protein gene is included within a 179-kilobase transcription unit: expression in the immune and central nervous systems.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10695-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10695. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 7504278 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic expression of the golli-myelin basic protein gene in the SJL/J mouse.J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Mar;57(1-2):93-9. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)00167-m. J Neuroimmunol. 1995. PMID: 7535793
-
Structure and developmental regulation of Golli-mbp, a 105-kilobase gene that encompasses the myelin basic protein gene and is expressed in cells in the oligodendrocyte lineage in the brain.J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4930-8. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 7680345
-
Molecular biology of myelin basic protein: gene rearrangement and expression of anti-sense RNA in myelin-deficient mutants.Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;98(1):51-61. Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991. PMID: 1709079 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic and Superimposed Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Fasudil in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Dec;60(4):486-497. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0819-3. Epub 2016 Aug 30. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27573128
-
Minireview: expression and function of golli protein in immune system.Neurochem Res. 2007 Feb;32(2):273-8. doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9164-1. Epub 2006 Oct 6. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17024569 Review.
-
An immunohistochemical identification key for cell types in adult mouse prostatic and urethral tissue sections.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 16;12(11):e0188413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188413. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29145476 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Golli-MBP expression in CNS macrophages during acute LPS-induced CNS inflammation and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE).ScientificWorldJournal. 2007 Nov 2;7:112-20. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2007.251. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007. PMID: 17982583 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of myelin protein genes during the development of the oligodendrocyte.ASN Neuro. 2010 Feb 1;2(1):e00027. doi: 10.1042/AN20090051. ASN Neuro. 2010. PMID: 20017732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grima B, Zelenika D, Pessac B. J Neurochem. 1992;59:2318–2323. - PubMed
-
- Zelenika D, Grima B, Pessac B. J Neurochem. 1993;60:1574–1577. - PubMed
-
- Grima B, Zelenika D, Pessac B. Neurobiol Dis. 1994;1:61–66. - PubMed
-
- Campagnoni A T, Pribyl T M, Campagnoni C W, Kampf K, Amur-Umarjee S, Landry C F, Handley V W, Newman S L, Garbay B, Kitamura K. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:4930–4938. - PubMed
-
- Kalwy S, Marty M C, Bausero P, Pessac B. J Neurochem. 1998;70:435–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

