Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53 --> Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice
- PMID: 12084935
- PMCID: PMC124407
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.132197599
Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53 --> Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice
Abstract
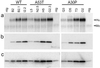
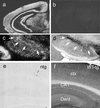
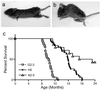
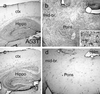
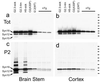
Mutations in alpha-synuclein (alpha-Syn) cause Parkinson's disease (PD) in a small number of pedigrees with familial PD. Moreover, alpha-Syn accumulates as a major component of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites, intraneuronal inclusions that are neuropathological hallmarks of PD. To better understand the pathogenic relationship between alterations in the biology of alpha-Syn and PD-associated neurodegeneration, we generated multiple lines of transgenic mice expressing high levels of either wild-type or familial PD-linked Ala-30 --> Pro (A30P) or Ala-53 --> Thr (A53T) human alpha-Syns. The mice expressing the A53T human alpha-Syn, but not wild-type or the A30P variants, develop adult-onset neurodegenerative disease with a progressive motoric dysfunction leading to death. Pathologically, affected mice exhibit neuronal abnormalities (in perikarya and neurites) including pathological accumulations of alpha-Syn and ubiquitin. Consistent with abnormal neuronal accumulation of alpha-Syn, brain regions with pathology exhibit increases in detergent-insoluble alpha-Syn and alpha-Syn aggregates. Our results demonstrate that the A53T mutant alpha-Syn causes significantly greater in vivo neurotoxicity as compared with other alpha-Syn variants. Further, alpha-Syn-dependent neurodegeneration is associated with abnormal accumulation of detergent-insoluble alpha-Syn.
Figures

References
-
- Fahn S, Przedborski S. In: Merritt's Neurology. Rowland L P, editor. Williams & Wilkins, New York: Lippincott; 2000. pp. 679–695.
-
- Polymeropoulos M H, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide S E, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, et al. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen J T, Schols L, Riess O. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- George J M, Clayton D F. Neurosci News. 1998;1:12–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

