Association of RET codon 691 polymorphism in radiation-induced human thyroid tumours with C-cell hyperplasia in peritumoural tissue
- PMID: 12085189
- PMCID: PMC2375427
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600371
Association of RET codon 691 polymorphism in radiation-induced human thyroid tumours with C-cell hyperplasia in peritumoural tissue
Abstract
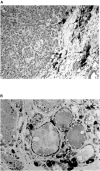
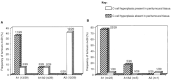
The RET proto-oncogene encodes a protein structurally related to transmembrane receptors with an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. In human thyroid gland, the RET proto-oncogene is normally expressed in parafollicular C-cells. Thyroid C-cell hyperplasia is associated with inherited medullary thyroid carcinomas and is considered as a pre-neoplastic stage of C-cells disease. It has also been observed in thyroid tissues adjacent to follicular and papillary carcinomas. In order to study the relationship between a misfunctioning of the RET proto-oncogene and the presence of C-cell hyperplasia, we compared a series of thyroid glands presenting sporadic or radiation-associated tumours, as well as samples of unrelated normal thyroid tissues, for alteration in exons 10 and 11 of the gene and for the presence or absence of C-cell hyperplasia. Here we report a significantly higher frequency of C-cell hyperplasia present in peritumoural thyroid tissues of radiation-induced epithelial thyroid tumours, than in peritumoural of sporadic thyroid tumours or in control normal thyroid tissues (P=0.001). A G691S RET polymorphism was present with a higher frequency in radiation-induced epithelial thyroid tumours (55%) than in sporadic tumours (20%) and in control normal thyroid tissues (15%). Interestingly, this polymorphism was associated in the majority (88%) of radiation-induced tumours with a C-cell hyperplasia in the peritumoural tissues. Several explanations for this association are discussed.
Copyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct pattern of ret oncogene rearrangements in morphological variants of radiation-induced and sporadic thyroid papillary carcinomas in children.Cancer Res. 1997 May 1;57(9):1690-4. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9135009
-
High prevalence of activating ret proto-oncogene rearrangements, in thyroid tumors from patients who had received external radiation.Oncogene. 1997 Sep;15(11):1263-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200206. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9315093
-
RET oncogene puzzle in Chernobyl thyroid tumours.Lancet. 1996 Apr 27;347(9009):1176. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90626-1. Lancet. 1996. PMID: 8609764 No abstract available.
-
Rearrangements of RET and NTRK1 tyrosine kinase receptors in papillary thyroid carcinomas.Recent Results Cancer Res. 1998;154:237-47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46870-4_15. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 10027004 Review.
-
The RET proto-oncogene in medullary and papillary thyroid carcinoma. Molecular features, pathophysiology and clinical implications.Virchows Arch. 1997 Jul;431(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s004280050062. Virchows Arch. 1997. PMID: 9247627 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a DHPLC-based assay for rapid detection of RET germline mutations in Italian patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma.J Endocrinol Invest. 2004 Feb;27(2):111-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03346254. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004. PMID: 15129804
-
A unique RET EXON 11 (G691S) polymorphism in an Indian patient with a collision tumor of the thyroid.Diagn Pathol. 2007 Oct 16;2:39. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-2-39. Diagn Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17939859 Free PMC article.
-
RET proto-oncogene mutations are restricted to codon 618 in Cypriot families with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2.J Endocrinol Invest. 2011 Nov;34(10):764-9. doi: 10.3275/7605. Epub 2011 Mar 21. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011. PMID: 21422799
-
RET gene mutations and polymorphisms in medullary thyroid carcinomas in Indian patients.J Biosci. 2011 Sep;36(4):603-11. doi: 10.1007/s12038-011-9095-0. J Biosci. 2011. PMID: 21857107
-
Functional RET G691S polymorphism in cutaneous malignant melanoma.Oncogene. 2009 Aug 27;28(34):3058-68. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.164. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19561646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AiraksinenMSTitievskyASaarmaM1999GDNF family neurotrophic factor signaling: four masters, one servant? Mol Cell Neurosci 13313325 - PubMed
-
- Albores-SaavedraJMonforteHNadjiMMoralesAR1988C-cell hyperplasia in thyroid tissue adjacent to follicular cell tumors Hum Pathol 19795799 - PubMed
-
- BalohRHEnomotoHJohnsonJrEMMilbrandtJ2000The GDNF family ligands and receptors - implications for neural development Curr Opin Neurobiol 10103110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

