Anti-angiogenic action of hyperthermia by suppressing gene expression and production of tumour-derived vascular endothelial growth factor in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 12085210
- PMCID: PMC2746582
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600268
Anti-angiogenic action of hyperthermia by suppressing gene expression and production of tumour-derived vascular endothelial growth factor in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
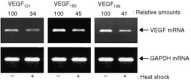
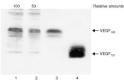
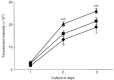
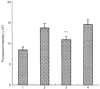
Vascular endothelial growth factor is an important angiogenic factor for tumour progression because it increases endothelial-cell proliferation and remodels extracellular matrix in blood vessels. We demonstrated that hyperthermia at 42 degrees C, termed heat shock, suppressed the gene expression and production of vascular endothelial growth factor in human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells and inhibited its in vitro angiogenic action on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The gene expression of alternative splicing variants for vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF121, VEGF165 and VEGF189, was constitutively detected in HT-1080 cells, but the VEGF189 transcript was less abundant than VEGF121 and VEGF165. When HT-1080 cells were treated with heat shock at 42 degrees C for 4 h and then maintained at 37 degrees C for another 24 h, the gene expression of all vascular endothelial growth factor variants was suppressed. In addition, HT-1080 cells were found to produce abundant VEGF165, but much less VEGF121, both of which were inhibited by heat shock. Furthermore, the level of vascular endothelial growth factor in sera from six cancer patients was significantly diminished 2-3 weeks after completion of whole-body hyperthermia at 42 degrees C (49.9+/-36.5 pg x ml(-1), P<0.01) as compared with that prior to the treatment (177.0+/-77.5 pg x ml(-1)). On the other hand, HT-1080 cell-conditioned medium showed vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent cell proliferative activity and the augmentation of pro-matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The augmentation of endothelial-cell proliferation and pro-matrix metalloproteinase-1 production was poor when human umbilical vein endothelial cells were treated with conditioned medium from heat-shocked HT-1080 cells. These results suggest that hyperthermia acts as an anti-angiogenic strategy by suppressing the expression of tumour-derived vascular endothelial growth factor production and thereby inhibiting endothelial-cell proliferation and extracellular matrix remodelling in blood vessels.
comCopyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures



Similar articles
-
The human myoepithelial cell displays a multifaceted anti-angiogenic phenotype.Oncogene. 2000 Jul 20;19(31):3449-59. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203677. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10918603
-
p73 Overexpression increases VEGF and reduces thrombospondin-1 production: implications for tumor angiogenesis.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 1;20(50):7293-300. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204896. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11704858
-
Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation.Cancer Res. 1999 Jul 15;59(14):3374-8. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10416597
-
Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors may be an alternative anti-angiogenic strategy in the treatment of liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Possible role of vascular endothelial growth factor.Tumour Biol. 2002 Nov-Dec;23(6):348-56. doi: 10.1159/000069792. Tumour Biol. 2002. PMID: 12677092 Review.
-
Control of vascular endothelial growth factor angiogenic activity by the extracellular matrix.Biol Cell. 1998 Sep;90(5):381-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1998.tb01047.x. Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9835012 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of phototherapeutic-based nanoparticles in colorectal cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;17(5):1361-1381. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.58773. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of the Cavity After Removal of Giant Cell Tumor of the Bone.Front Surg. 2021 Jul 29;8:626272. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.626272. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34395504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperthermia inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep 14;18(34):4781-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4781. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23002349 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Polymer Phase Transition Behavior on Temperature-Responsive Polymer-Modified Liposomes for siRNA Transfection.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 19;20(2):430. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020430. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669495 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of mild hyperthermia plus docetaxel therapy on ER(+/-) breast cancer cells and action mechanisms.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Dec;33(6):870-876. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1214-8. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24337851
References
-
- AbrahamJAMergiaAWhangJLTumoloAFriedmanJHjerrildKAGospodarowiczDFiddesJC1986Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor Science 233545548 - PubMed
-
- AhmedSAGogalJrRMWalshJE1994A new rapid and simple non-radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: An alternative to [3H]thymidine incorporation assay J Immunol Methods 170211224 - PubMed
-
- AsanoMYukitaAMatsumotoTKondoSSuzukiH1995Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis by an immunoneutralizing monoclonal antibody to human vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor121 Cancer Res 5552965301 - PubMed
-
- BorgstromPHillanKJSriramaraoPFerraraN1996Complete inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of microtumors by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor neutralizing antibody: Novel concepts of angiostatic therapy from intravital videomicroscopy Cancer Res 5640324039 - PubMed
-
- CellierMFTaimiMChateauMTCannatAMartiJ1993Thermal stress as an inducer of differentiation of U937 cells Leukemia Res 17649656 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

