Orthogonal polarisation spectral imaging as a new tool for the assessment of antivascular tumour treatment in vivo: a validation study
- PMID: 12085213
- PMCID: PMC2746600
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600318
Orthogonal polarisation spectral imaging as a new tool for the assessment of antivascular tumour treatment in vivo: a validation study
Abstract
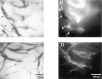
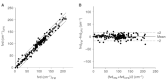
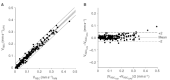
Tumour angiogenesis plays a key role in tumour growth, formation of metastasis, detection and treatment of malignant tumours. Recent investigations provided increasing evidence that quantitative analysis of tumour angiogenesis is an indispensable prerequisite for developing novel treatment strategies such as anti-angiogenic and antivascular treatment options. Therefore, it was our aim to establish and validate a new and versatile imaging technique, that is orthogonal polarisation spectral imaging, allowing for non-invasive quantitative imaging of tumour angiogenesis in vivo. Experiments were performed in amelanotic melanoma A-MEL 3 implanted in a transparent dorsal skinfold chamber of the hamster. Starting at day 0 after tumour cell implantation, animals were treated daily with the anti-angiogenic compound SU5416 (25 mg kg x bw(-1)) or vehicle (control) only. Functional vessel density, diameter of microvessels and red blood cell velocity were visualised by both orthogonal polarisation spectral imaging and fluorescence microscopy and analysed using a digital image system. The morphological and functional properties of the tumour microvasculature could be clearly identified by orthogonal polarisation spectral imaging. Data for functional vessel density correlated excellently with data obtained by fluorescence microscopy (y=0.99x+0.48, r2=0.97, R(S)=0.98, precision: 8.22 cm(-1) and bias: -0.32 cm(-1)). Correlation parameters for diameter of microvessels and red blood cell velocity were similar (r2=0.97, R(S)=0.99 and r2=0.93, R(S)=0.94 for diameter of microvessels and red blood cell velocity, respectively). Treatment with SU5416 reduced tumour angiogenesis. At day 3 and 6 after tumour cell implantation, respectively, functional vessel density was 4.8+/-2.1 and 87.2+/-10.2 cm(-1) compared to values of control animals of 66.6+/-10.1 and 147.4+/-13.2 cm(-1), respectively. In addition to the inhibition of tumour angiogenesis, tumour growth and the development of metastasis was strongly reduced in SU5416 treated animals. This new approach enables non-invasive, repeated and quantitative assessment of tumour vascular network and the effects of antiangiogenic treatment on tumour vasculature in vivo. Thus, quantification of tumour angiogenesis can be used to more accurately classify and monitor tumour biologic characteristics, and to explore aggressiveness of tumours.
comCopyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated assessment of tumour microvascular architecture in vivo.Anticancer Res. 2010 Jul;30(7):2597-602. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20682988
-
Antiangiogenic combination tumor therapy blocking alpha(v)-integrins and VEGF-receptor-2 increases therapeutic effects in vivo.Int J Cancer. 2006 Jul 15;119(2):423-31. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21838. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16477628
-
The low-molecular-weight heparin, nadroparin, inhibits tumour angiogenesis in a rodent dorsal skinfold chamber model.Br J Cancer. 2010 Mar 2;102(5):837-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605535. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20125158 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary ultrastructure and microcirculatory function of malignant tumors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;242:205-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8935-4_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988. PMID: 2469314 Review. No abstract available.
-
Surrogate biomarkers in evaluating response to anti-angiogenic agents: focus on sunitinib.Ann Oncol. 2007 Sep;18 Suppl 10:x11-9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm409. Ann Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17761718 Review.
Cited by
-
Automatic detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma on pathologic slides using polarized hyperspectral imaging and machine learning.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2021 Feb;11603:116030Q. doi: 10.1117/12.2582330. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2021. PMID: 34955584 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogonal polarization spectroscopy to detect mesenteric hypoperfusion.Intensive Care Med. 2008 Oct;34(10):1883-90. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1130-8. Epub 2008 May 31. Intensive Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18516589
-
Polarized hyperspectral microscopic imaging system for enhancing the visualization of collagen fibers and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Jan;29(1):016005. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.1.016005. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 38239390 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma on pathologic slides using polarized hyperspectral imaging and deep learning.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022 Feb-Mar;12039:120390G. doi: 10.1117/12.2614624. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022. PMID: 36798940 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic chemotherapy: possible clinical application in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2013 Oct 1;6(5):511-9. doi: 10.1593/tlo.13481. eCollection 2013. Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24151531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AsaishiKEndrichBGoetzAMessmerK1981Quantitative analysis of microvascular structure and function in the amelanotic melanoma A-Mel-3 Cancer Res 4118981904 - PubMed
-
- BergersGJahaherianKLoKMFolkmanJHanahanD1999Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice Science 284808812 - PubMed
-
- BlandJMAltmanDG1986Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement Lancet 1307310 - PubMed
-
- DellianMWalentaSGamarraFKuhnleGEMueller-KlieserWGoetzAE1994High-energy shock waves enhance hyperthermic response of tumors: effects on blood flow, energy metabolism, and tumor growth J Natl Cancer Inst 86287293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

