Inhibition of renal cell carcinoma angiogenesis and growth by antisense oligonucleotides targeting vascular endothelial growth factor
- PMID: 12085267
- PMCID: PMC2364273
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600416
Inhibition of renal cell carcinoma angiogenesis and growth by antisense oligonucleotides targeting vascular endothelial growth factor
Abstract
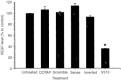
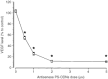
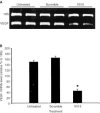
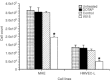
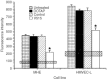
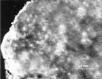
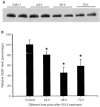
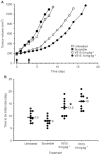
Angiogenesis is critical for growth and metastatic spread of solid tumours. It is tightly controlled by specific regulatory factors. Vascular endothelial growth factor has been implicated as the key factor in tumour angiogenesis. In the present studies we evaluated the effects of blocking vascular endothelial growth factor production by antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides on the growth and angiogenic activity of a pre-clinical model of renal cell carcinoma (Caki-1). In vitro studies showed that treating Caki-1 cells with antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides directed against vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA led to a reduction in expressed vascular endothelial growth factor levels sufficient to impair the proliferation and migration of co-cultured endothelial cells. The observed effects were antisense sequence specific, dose dependent, and could be achieved at a low, non-toxic concentration of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. When vascular endothelial growth factor antisense treated Caki-1 cells were injected into nude mice and evaluated for their angiogenic potential, the number of vessels initiated were approximately half that induced by untreated Caki-1 cells. To test the anti-tumour efficacy of vascular endothelial growth factor antisense, phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides were administrated to nude mice bearing macroscopic Caki-1 xenografts. The results showed that the systemic administration of two doses of vascular endothelial growth factor antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides given 1 and 4 days after the tumours reached a size of approximately 200 mm(3) significantly increased the time for tumours to grow to 1000 mm(3).
Copyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell-surface perturbations of the epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors by phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jun 10;94(12):6523-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6523. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9177251 Free PMC article.
-
Oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit retinal neovascularization in a murine model of proliferative retinopathy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4851-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4851. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8643492 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor C225 monoclonal antibody in combination with vascular endothelial growth factor antisense oligonucleotide in human GEO colon cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Sep;6(9):3739-47. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10999768
-
Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), an emerging target for cancer chemotherapy.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003 Mar;3(2):95-117. doi: 10.2174/1568011033353452. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003. PMID: 12678905 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor: an important angiogenic mediator in bladder cancer.Eur Urol. 1999 Jan;35(1):2-8. doi: 10.1159/000019811. Eur Urol. 1999. PMID: 9933788 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene therapy and kidney diseases.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Sep 6;32(4):101333. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101333. eCollection 2024 Dec 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39434922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Src-signaling interference impairs the dissemination of blood-borne tumor cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Aug;349(2):541-50. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1415-7. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22526632 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for urologic tumors.Curr Urol Rep. 2003 Feb;4(1):60-9. doi: 10.1007/s11934-003-0059-2. Curr Urol Rep. 2003. PMID: 12537941 Review.
-
Kidney Cancer and Chronic Kidney Disease: Too Close for Comfort.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 24;9(12):1761. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121761. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel decoy receptor fusion protein for FGF-2 potently inhibits tumour growth.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jul 8;111(1):68-77. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.282. Epub 2014 May 29. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24874473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AsanoMYukitaAMatsumotoTKondoSSuzukiH1995Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis by an immunoneutralizing monoclonal antibody to human vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor121 Cancer Res 5552965301 - PubMed
-
- BaccalaAAZhongHCliftSMNelsonWGMarshallFFPasseTJGambillNBSimonsJW1998Serum vascular endothelial growth factor is a candidate biomarker of metastatic tumor response to ex vivo gene therapy of renal cell cancer Urology 51327332 - PubMed
-
- BellettiBFerraroPArraCBaldassarreGBruniPStaibanoSDe RosaGSalvatoreGFuscoAPersicoMGVigliettoG1999Modulation of in vivo growth of thyroid tumor-derived cell lines by sense and antisense vascular endothelial growth factor gene Oncogene 1848604869 - PubMed
-
- BergerDPHerbstrittLDenglerWAMarmeDMertelsmannRFiebigHH1995Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA expression in human tumor models of different histologies Ann Oncol 6817825 - PubMed
-
- BicknellRHarrisAL1992Anticancer strategies involving the vasculature: vascular targeting and the inhibition of angiogenesis Semin Cancer Bol 3399407 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

