Insertion of a small peptide of six amino acids into the beta7-beta8 loop of the p51 subunit of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase perturbs the heterodimer and affects its activities
- PMID: 12086585
- PMCID: PMC117134
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-3-18
Insertion of a small peptide of six amino acids into the beta7-beta8 loop of the p51 subunit of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase perturbs the heterodimer and affects its activities
Abstract
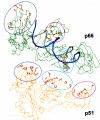
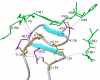
Background: HIV-1 RT is a heterodimeric enzyme, comprising of the p66 and p51 subunits. Earlier, we have shown that the beta7-beta8 loop of p51 is a key structural element for RT dimerization (Pandey et al., Biochemistry 40: 9505, 2001). Deletion or alanine substitution of four amino acid residues of this loop in the p51 subunit severely impaired DNA binding and catalytic activities of the enzyme. To further examine the role of this loop in HIV-1 RT, we have increased its size such that the six amino acids loop sequences are repeated in tandem and examined its impact on the dimerization process and catalytic function of the enzyme.
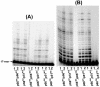
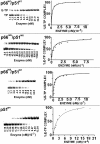
Results: The polymerase and the RNase H activities of HIV-1 RT carrying insertion in the beta7-beta8 loop of both the subunits (p66INS/p51INS) were severely impaired with substantial loss of DNA binding ability. These enzymatic activities were restored when the mutant p66INS subunit was dimerized with the wild type p51. Glycerol gradient sedimentation analysis revealed that the mutant p51INS subunit was unable to form stable dimer either with the wild type p66 or mutant p66INS. Furthermore, the p66INS/p66INS mutant sedimented as a monomeric species, suggesting its inability to form stable homodimer.
Conclusion: The data presented herein indicates that any perturbation in the beta7-beta8 loop of the p51 subunit of HIV-1 RT affects the dimerization process resulting in substantial loss of DNA binding ability and catalytic function of the enzyme.
Figures



References
-
- Muller B, Restle T, Weiss S, Gautel M, Sczakiel G, Goody R. Co-expression of the subunits of the heterodimer of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:13975–13978. - PubMed
-
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumor Viruses. Nature. 1970;226:1209–1211. - PubMed
-
- Temin HM, Mizytani S. RNA-directed DNA polymerase in virions of Rouse sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970;226:2111–1213. - PubMed
-
- Farmerie WG, Leob D, Casavant NC, Hutchinson CAd, Egell MH, Swanstrom R. Expression and processing of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase in E. coli. Science. 1987;236:305–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

