USF2 inhibits C/EBP-mediated transcriptional regulation of the RIIbeta subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase
- PMID: 12086590
- PMCID: PMC117135
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-3-10
USF2 inhibits C/EBP-mediated transcriptional regulation of the RIIbeta subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase
Abstract
Background: Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) plays a central role in regulation of energy metabolism. Upon stimulation of testicular Sertoli cells by follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), glycolysis is activated to increase the production of nutrients for the germ cells, and a new regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, RIIbeta, is induced. We have previously shown that production of the transcription factor C/EBPbeta is rapidly increased by FSH and cAMP in primary Sertoli cell cultures, and that C/EBPbeta induces the RIIbeta promoter.
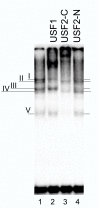
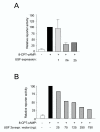
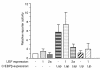
Results: In this work we show that USF1, USF2 and truncated USF isoforms bind to a conserved E-box in the RIIbeta gene. Interestingly, overexpression of USF2, but not USF1, led to inhibition of both cAMP- and C/EBPbeta-mediated induction of RIIbeta. Furthermore, Western blots show that a novel USF1 isoform is induced by cAMP in Sertoli cells.
Conclusions: These results indicate that the expression of various USF isoforms may be regulated by cAMP, and that the interplay between USF and C/EBPbeta is important for cAMP-mediated regulation of RIIbeta expression. The counteracting effects of USF2 and C/EBPbeta observed on the RIIbeta promoter is in accordance with the hypothesis that C/EBP and USF play opposite roles in regulation of glucose metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the 5'-flanking region of the gene for the cAMP-inducible protein kinase A subunit, RIIbeta, in Sertoli cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997 Apr 25;129(1):101-14. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(97)04045-8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9175634
-
Method of transfection affects the cAMP-mediated induction of the RIIbeta subunit of protein kinase A in Sertoli cells: inhibition of response by increase in intracellullar calcium.Eur J Endocrinol. 1999 Jul;141(1):75-82. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1410075. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10407227
-
Selective modulation of protein kinase A I and II reveals distinct roles in thyroid cell gene expression and growth.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Dec;20(12):3196-211. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0493. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16887886
-
The RIIbeta regulatory subunit of protein kinase A binds to cAMP response element: an alternative cAMP signaling pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 9;95(12):6687-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6687. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9618473 Free PMC article.
-
Marker genes of decidualization: activation of the decidual prolactin gene.Hum Reprod Update. 1998 Sep-Oct;4(5):472-9. doi: 10.1093/humupd/4.5.472. Hum Reprod Update. 1998. PMID: 10027598 Review.
Cited by
-
Data recovery and integration from public databases uncovers transformation-specific transcriptional downregulation of cAMP-PKA pathway-encoding genes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 15;10 Suppl 12(Suppl 12):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S12-S1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19828069 Free PMC article.
-
USF2-mediated upregulation of TXNRD1 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating Akt/mTOR signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 1;13(11):917. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05363-x. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36319631 Free PMC article.
-
A functional genomics pipeline identifies pleiotropy and cross-tissue effects within obesity-associated GWAS loci.Nat Commun. 2021 Sep 6;12(1):5253. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25614-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34489471 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated C/EBPβ influences a complex network involving YY1 and USF2 in lung epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060211. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fakunding JL, Tindall DJ, Dedman JR, Mena CR, Means AR. Biochemical actions of follice-stimulating hormone in the sertoli cell of the rat testis. Endocrinology. 1976;98:392–402. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

