Tonic inhibitory control exerted by opioid peptides in the paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus on regional hemodynamic activity in rats
- PMID: 12086985
- PMCID: PMC1573405
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704780
Tonic inhibitory control exerted by opioid peptides in the paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus on regional hemodynamic activity in rats
Abstract
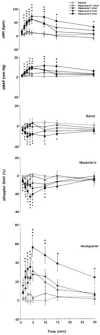
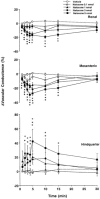
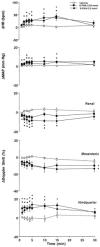
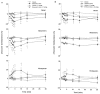
1. Systemic and regional cardiovascular changes were measured following bilateral microinjection of specific and selective opioid-receptor antagonists into the paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus (PVN) of awake, freely moving rats. 2. PVN microinjection of increasing doses of the specific opioid antagonist naloxone - methiodide (1 - 5.0 nmol), or a selective mu-opioid receptor antagonist, beta-funaltrexamine (0.05 - 0.5 nmol), evoked important cardiovascular changes characterized by small and transient increases in heart rate (HR) and mean arterial pressure (MAP), vasoconstriction in renal and superior mesenteric vascular beds and vasodilation in the hindquarter vascular bed. 3. No significant cardiovascular changes were observed following PVN administration of the highly selective delta-opioid-receptor antagonist, ICI 174864 (0.1 - 1 nmol), or the selective kappa-opioid-receptor antagonist, nor-binaltorphine (0.1 - 1 nmol). 4. Most of the cardiovascular responses to naloxone (3 nmol) and beta-funaltrexamine (0.5 nmol) were attenuated or abolished by an i.v. treatment with a specific vasopressin V(1) receptor antagonist. 5. These results suggest that endogenous opioid peptides and mu-type PVN opioid receptors modulate a tonically-active central depressor pathway acting on systemic and regional haemodynamic systems. Part of this influence could involve a tonic inhibition of vasopressin release.
Figures



References
-
- APPEL N.M., KIRITSY-ROY J.A., VAN LOON G.R. μ-opioid receptors at discrete hypothalamic and brainstem sites mediate opioid peptide induced increases in central sympathetic out flow. Brain Res. 1986;378:8–20. - PubMed
-
- ARNAULD E., CIRINO M., LAYTON B.S., RENAULD L.P. Contrasting actions of amino acids, acetylcholine, noradrenaline and leucine enkephalin on the excitability of supraoptic vasopressin-secreting neurons. Neuroendocrinol. 1983;36:187–196. - PubMed
-
- BACHELARD H., PITRE M., LESSARD A. Mechanisms of the regional hemodynamic effects of a mu-opioid receptor agonist microinjected into the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei of conscious unrestrained rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997;280:460–470. - PubMed
-
- BOULOUX P.M.G.Cardiovascular responses to stress: the role of opioid peptides Baillière's Clinical endocrinology and metabolism 1987London: Baillière Tindall; 439–465.ed. Grossman, A., pp - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

