Comparison of the expression of calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) with CGRP and adrenomedullin binding in cell lines
- PMID: 12086988
- PMCID: PMC1573393
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704761
Comparison of the expression of calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) with CGRP and adrenomedullin binding in cell lines
Abstract
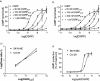
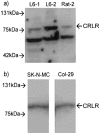
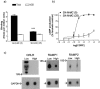
1. The calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and specific receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) together form receptors for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and/or adrenomedullin in transfected cells. 2. There is less evidence that innate CGRP and adrenomedullin receptors are formed by CRLR/RAMP combinations. We therefore examined whether CGRP and/or adrenomedullin binding correlated with CRLR and RAMP mRNA expression in human and rat cell lines known to express these receptors. Specific human or rat CRLR antibodies were used to examine the presence of CRLR in these cells. 3. We confirmed CGRP subtype 1 receptor (CGRP(1)) pharmacology in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells. L6 myoblast cells expressed both CGRP(1) and adrenomedullin receptors whereas Rat-2 fibroblasts expressed only adrenomedullin receptors. In contrast we could not confirm CGRP(2) receptor pharmacology for Col-29 colonic epithelial cells, which, instead were CGRP(1)-like in this study. 4. L6, SK-N-MC and Col-29 cells expressed mRNA for RAMP1 and RAMP2 but Rat-2 fibroblasts had only RAMP2. No cell line had detectable RAMP3 mRNA. 5. SK-N-MC, Col-29 and Rat-2 fibroblast cells expressed CRLR mRNA. By contrast, CRLR mRNA was undetectable by Northern analysis in one source of L6 cells. Conversely, a different source of L6 cells had mRNA for CRLR. All of the cell lines expressed CRLR protein. Thus, circumstances where CRLR mRNA is apparently absent by Northern analysis do not exclude the presence of this receptor. 6. These data strongly support CRLR, together with appropriate RAMPs as binding sites for CGRP and adrenomedullin in cultured cells.
Figures
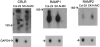
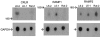
Similar articles
-
A comparison of the actions of BIBN4096BS and CGRP(8-37) on CGRP and adrenomedullin receptors expressed on SK-N-MC, L6, Col 29 and Rat 2 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Sep;137(1):80-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704844. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12183333 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the expression of calcitonin receptor-like receptor, receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) 1, RAMP2, and RAMP3 in rat uterus during pregnancy, labor, and by steroid hormone treatments.Biol Reprod. 2003 Oct;69(4):1432-7. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.015628. Epub 2003 Jun 11. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12801991
-
Progesterone upregulates calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptor components and cyclic adenosine 3'5'-monophosphate generation in Eker rat uterine smooth muscle cell line.Biol Reprod. 2005 Feb;72(2):416-22. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.033779. Epub 2004 Oct 6. Biol Reprod. 2005. PMID: 15469997
-
Functional interaction of G protein-coupled receptors of the adrenomedullin peptide family with accessory receptor-activity-modifying proteins (RAMP).Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Apr 1;57(1):14-22. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10051. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 11921352 Review.
-
Adrenomedullin and related peptides: receptors and accessory proteins.Peptides. 2001 Nov;22(11):1765-72. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00515-0. Peptides. 2001. PMID: 11754962 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison of the actions of BIBN4096BS and CGRP(8-37) on CGRP and adrenomedullin receptors expressed on SK-N-MC, L6, Col 29 and Rat 2 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Sep;137(1):80-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704844. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12183333 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of endothelial and epithelial barrier functions by peptide hormones of the adrenomedullin family.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Aug 25;4(4):e1228439. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1228439. eCollection 2016. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 28123925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGRP in the trigeminovascular system: a role for CGRP, adrenomedullin and amylin receptors?Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(7):1293-307. doi: 10.1111/bph.12129. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23425327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipidated Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Peptide Antagonists Retain CGRP Receptor Activity and Attenuate CGRP Action In Vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 7;13:832589. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.832589. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35341216 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide: physiology and pathophysiology.Physiol Rev. 2014 Oct;94(4):1099-142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00034.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25287861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ABBOTT C.R., ROSSI M., KIM M., ALAHMED S.H., TAYLOR G.M., GHATEI M.A., SMITH D.M., BLOOM S.R. Investigation of the melanocyte stimulating hormones on food intake. Lack of evidence to support a role for the melanocortin-3 receptor. Brain Res. 2000;869:203–210. - PubMed
-
- BHOGAL R., SMITH D.M., PURKISS P., BLOOM S.R. Molecular identification of binding sites for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) in mammalian lung: species variation and binding of truncated CGRP and IAPP. Endocrinology. 1993;133:2351–2361. - PubMed
-
- BRAIN S.D., CAMBRIDGE H. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: vasoactive effects and potential therapeutic role. Gen. Pharmacol. 1996;27:607–611. - PubMed
-
- BUHLMANN N., LEUTHAUSER K., MUFF R., FISCHER J.A., BORN W. A receptor activity modifying protein (RAMP)2-dependent adrenomedullin receptor is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor when coexpressed with human RAMP1. Endocrinology. 1999;140:2883–2890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

