Spontaneous and double-strand break-induced recombination, and gene conversion tract lengths, are differentially affected by overexpression of wild-type or ATPase-defective yeast Rad54
- PMID: 12087154
- PMCID: PMC117068
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf413
Spontaneous and double-strand break-induced recombination, and gene conversion tract lengths, are differentially affected by overexpression of wild-type or ATPase-defective yeast Rad54
Abstract
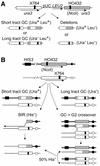
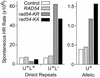
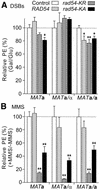
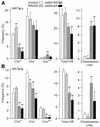
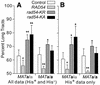
Rad54 plays key roles in homologous recombination (HR) and double-strand break (DSB) repair in yeast, along with Rad51, Rad52, Rad55 and Rad57. Rad54 belongs to the Swi2/Snf2 family of DNA-stimulated ATPases. Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments catalyze DNA strand exchange and Rad54 augments this activity of Rad51. Mutations in the Rad54 ATPase domain (ATPase(-)) impair Rad54 function in vitro, sensitize yeast to killing by methylmethane sulfonate and reduce spontaneous gene conversion. We found that overexpression of ATPase(-) Rad54 reduced spontaneous direct repeat gene conversion and increased both spontaneous direct repeat deletion and spontaneous allelic conversion. Overexpression of ATPase(-) Rad54 decreased DSB-induced allelic conversion, but increased chromosome loss and DSB-dependent lethality. Thus, ATP hydrolysis by Rad54 contributes to genome stability by promoting high-fidelity DSB repair and suppressing spontaneous deletions. Overexpression of wild-type Rad54 did not alter DSB-induced HR levels, but conversion tract lengths were reduced. Interestingly, ATPase(-) Rad54 decreased overall HR levels and increased tract lengths. These tract length changes provide new in vivo evidence that Rad54 functions in the post-synaptic phase during recombinational repair of DSBs.
Figures

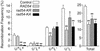
References
-
- Mazin A.V., Bornarth,C.J., Solinger,J.A., Heyer,W.D. and Kowalczykowski,S.C. (2000) Rad54 protein is targeted to pairing loci by the Rad51 nucleoprotein filament. Mol. Cell, 6, 583–592. - PubMed
-
- Sung P. (1997) Yeast Rad55 and Rad57 proteins form a heterodimer that functions with replication protein A to promote DNA strand exchange by Rad51 recombinase. Genes Dev., 11, 1111–1121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

