Quantitative stability of DNA after extended storage of clinical specimens as determined by real-time PCR
- PMID: 12089286
- PMCID: PMC120597
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2609-2611.2002
Quantitative stability of DNA after extended storage of clinical specimens as determined by real-time PCR
Abstract
Viral DNA stored for extended periods can be amplified by PCR. However, it is unknown whether stored specimens give accurate quantitative results by newer real-time PCR techniques. We therefore compared herpes simplex virus DNA levels in specimens before and after 16 months of storage. The levels of viral DNA remained stable whether the DNA was stored as purified DNA or unextracted DNA in a whole specimen.
Figures
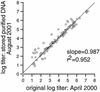

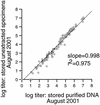
References
-
- Cuypers, H. T. M., D. Bresters, I. N. Winkel, H. W. Reesink, A. J. Weiner, M. Houghton, C. L. van der Poel, and P. N. Lelie. 1992. Storage conditions of blood samples and primer selection affect the yield of cDNA polymerase chain reaction products of hepatitis C virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30:3220-3224. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Farkas, D. H., A. M. Drevon, F. L. Kiechle, R. G. DiCarlo, E. M. Heath, and D. Crisan. 1996. Specimen stability for DNA-based diagnostic testing. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 5:227-235. - PubMed
-
- Farkas, D. H., K. L. Kaul, D. L. Wiedbrauk, and F. L. Kiechle. 1996. Specimen collection and storage for diagnostic molecular pathology investigation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 120:591-596. - PubMed
-
- Halfon, P., H. Khiri, V. Gerolami, M. Bourliere, J. M. Feryn, P. Peynier, A. Gauthier, and G. Cartouzou. 1996. Impact of various handling and storage conditions on quantitative detection of hepatitis C virus RNA. J. Hepatol. 25:307-311. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

