Predominant selection of T cells specific for the glycosylated collagen type II epitope (263-270) in humanized transgenic mice and in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 12089323
- PMCID: PMC126607
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.132254199
Predominant selection of T cells specific for the glycosylated collagen type II epitope (263-270) in humanized transgenic mice and in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with certain MHC class II alleles and is characterized by a chronic autoimmune response in the joints. Using transgenic mice expressing human DR4 (DRB1*0401) and human CD4, but lacking endogenous MHC class II, we show that posttranslational glycosylation of type II collagen (CII) influences the level of T cell tolerance to this candidate cartilage-specific autoantigen. In such mice, the expression of human CII resulted in a tolerized murine T cell response to human CII. However, tolerance induction remained incomplete, preferentially deleting responses to the nonmodified CII 263-270 epitope, whereas T cell recognition of a glycosylated variant of this epitope was affected to a lesser degree. A similar dominance of T cell responses to CII-glycopeptides was recorded in a cohort of severely affected RA-patients (n = 14). Thus, RA T cells predominantly recognize the immunodominant CII peptide in its glycosylated form and may explain why previously it has been difficult to detect T cell responses to CII in RA patients.
Figures
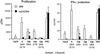



Comment in
-
Processing of glycans on glycoprotein and glycopeptide antigens in antigen-presenting cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 23;99(15):9611-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152345899. Epub 2002 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12122209 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The impact of glycosylation on HLA-DR1-restricted T cell recognition of type II collagen in a mouse model.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Feb;54(2):482-91. doi: 10.1002/art.21565. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16447222
-
Glycosylation of type II collagen is of major importance for T cell tolerance and pathology in collagen-induced arthritis.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Dec;32(12):3776-84. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200212)32:12<3776::AID-IMMU3776>3.0.CO;2-A. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12516572
-
Association between protein tyrosine phosphatase 22 variant R620W in conjunction with the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and humoral autoimmunity to an immunodominant epitope of cartilage-specific type II collagen in early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Jan;54(1):82-9. doi: 10.1002/art.21498. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16385499
-
Immunopathogenesis of collagen arthritis.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003 Aug;25(1):3-18. doi: 10.1007/s00281-003-0127-1. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003. PMID: 12904888 Review.
-
Exploring the reciprocal relationship between immunity and inflammation in chronic inflammatory arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 Jun;42(6):716-31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg262. Epub 2003 Mar 31. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003. PMID: 12730506 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into spatial configuration of a galactosylated epitope required to trigger arthritogenic T-cell receptors specific for the sugar moiety.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(5):R92. doi: 10.1186/ar2291. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17848196 Free PMC article.
-
A single functional group substitution in c5a breaks B cell and T cell tolerance and protects against experimental arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Mar;66(3):610-21. doi: 10.1002/art.38237. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24574221 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis for Studies on Immunopathogenesis and Preclinical Testing of Cell-Based Therapies.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00203. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30837986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapy targeting antigen-specific T cells by a peptide-based tolerizing vaccine against autoimmune arthritis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 20;120(25):e2218668120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218668120. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37307481 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a B-cell-dependent chronic arthritis with glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(6):R1316-24. doi: 10.1186/ar1829. Epub 2005 Sep 20. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 16277685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fugger L, Rothbard J B, Sonderstrup McDevitt G. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:928–933. - PubMed
-
- Rosloniec E F, Brand D D, Myers L K, Esaki Y, Whittington K B, Zaller D M, Woods A, Stuart J M, Kang A H. J Immunol. 1998;160:2573–2578. - PubMed
-
- Kim H Y, Kim W U, Cho M L, Lee S K, Youn J, Kim S I, Yoo W H, Park J H, Min J K, Lee S H, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:2085–2093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

