Full-length messenger RNA sequences greatly improve genome annotation
- PMID: 12093376
- PMCID: PMC116726
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-6-research0029
Full-length messenger RNA sequences greatly improve genome annotation
Abstract
Background: Annotation of eukaryotic genomes is a complex endeavor that requires the integration of evidence from multiple, often contradictory, sources. With the ever-increasing amount of genome sequence data now available, methods for accurate identification of large numbers of genes have become urgently needed. In an effort to create a set of very high-quality gene models, we used the sequence of 5,000 full-length gene transcripts from Arabidopsis to re-annotate its genome. We have mapped these transcripts to their exact chromosomal locations and, using alignment programs, have created gene models that provide a reference set for this organism.
Results: Approximately 35% of the transcripts indicated that previously annotated genes needed modification, and 5% of the transcripts represented newly discovered genes. We also discovered that multiple transcription initiation sites appear to be much more common than previously known, and we report numerous cases of alternative mRNA splicing. We include a comparison of different alignment software and an analysis of how the transcript data improved the previously published annotation.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that sequencing of large numbers of full-length transcripts followed by computational mapping greatly improves identification of the complete exon structures of eukaryotic genes. In addition, we are able to find numerous introns in the untranslated regions of the genes.
Figures

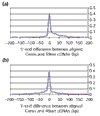
References
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, Smith HO, Yandell M, Evans CA, Holt RA, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

