Antigenicity of Leishmania braziliensis histone H1 during cutaneous leishmaniasis: localization of antigenic determinants
- PMID: 12093677
- PMCID: PMC120041
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.9.4.808-811.2002
Antigenicity of Leishmania braziliensis histone H1 during cutaneous leishmaniasis: localization of antigenic determinants
Abstract
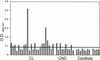
The humoral immune response against Leishmania braziliensis histone H1 by patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis is described. For this purpose, the protein was purified as a recombinant protein in a prokaryotic expression system and was assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with a collection of sera from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis and Chagas' disease. The assays showed that L. braziliensis histone H1 was recognized by 66% of the serum samples from patients with leishmaniasis and by 40% of the serum samples from patients with Chagas' disease, indicating that it acts as an immunogen during cutaneous leishmaniasis. In order to locate the linear antigenic determinants of this protein, a collection of synthetic peptides covering the L. braziliensis histone H1sequence was tested by ELISA. The experiments showed that the main antigenic determinant is located in the central region of this protein. Our results show that the recombinant L. braziliensis histone H1 is recognized by a significant percentage of serum samples from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis, but use of this protein as a tool for the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis is hampered by the cross-reaction with sera from patients with Chagas' disease.
Figures
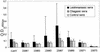
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the antigenic properties of the L. infantum Hsp70: design of synthetic peptides for specific serodiagnosis of human leishmaniasis.Immunol Lett. 1998 Oct;63(3):169-74. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(98)00071-6. Immunol Lett. 1998. PMID: 9840686
-
Analysis of the specificity of human antibodies to antigens of Leishmania braziliensis braziliensis.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1989 Jul-Aug;31(4):228-34. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651989000400004. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1989. PMID: 2626643
-
The sera from individuals suffering from cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania brazilensis present antibodies against parasitic conserved proteins, but not their human counterparts.Parasite. 2006 Sep;13(3):231-6. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2006133231. Parasite. 2006. PMID: 17007215
-
Diagnostic accuracy of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays to detect anti-Leishmania antibodies in patients with American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis: a systematic review.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2019 Aug 19;61:e42. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946201961042. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2019. PMID: 31432991 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome Activation by CD8+ T Cells from Patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania braziliensis in the Immunopathogenesis of the Disease.J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Jan;141(1):209-213.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.05.106. Epub 2020 Jun 13. J Invest Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32544477 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Potential antigenic targets used in immunological tests for diagnosis of tegumentary leishmaniasis: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2021 May 27;16(5):e0251956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251956. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34043671 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel Leishmania major antigens that elicit IgG2a response in resistant and susceptible mice.Korean J Parasitol. 2006 Mar;44(1):43-8. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2006.44.1.43. Korean J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16514281 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with L. infantum chagasi nucleosomal histones confers protection against new world cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania braziliensis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052296. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284976 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a more precise serological diagnosis of human tegumentary leishmaniasis using Leishmania recombinant proteins.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 12;8(6):e66110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066110. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776617 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis by Leishmania extract: identification of a disease-associated antibody specificity.BMC Res Notes. 2015 May 14;8:197. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1158-0. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 25971623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslund, L., L. Carlsson, J. Henriksson, M. Rydoiker, G. C. Toro, N. Galanti, and U. Petterson. 1994. A gene family encoding heterogeneous histone H1 proteins in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 65:317-330. - PubMed
-
- Burri, M., W. Schlimme, B. Betschart, U. Kampfer, J. Schaller, and H. Hecker. 1993. Biochemical and functional characterization of histone H1-like proteins in procyclic Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Parasitol. Res. 79:649-659. - PubMed
-
- Cerdeñosa, N., C. Riera, P. Cortés, F. March, C. Muñoz, M. Portús, and G. Prats. 1995. Detection and characterization by immunoblot analysis of potentially diagnostic Leishmania infantum polypeptides in human visceral leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 17:509-516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

